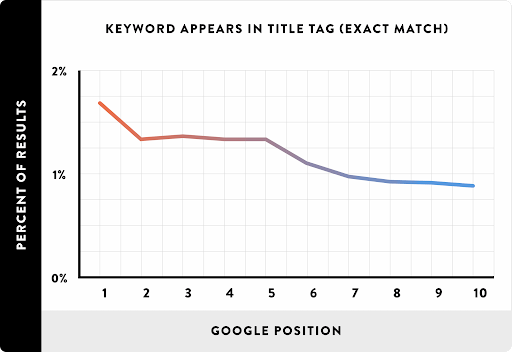
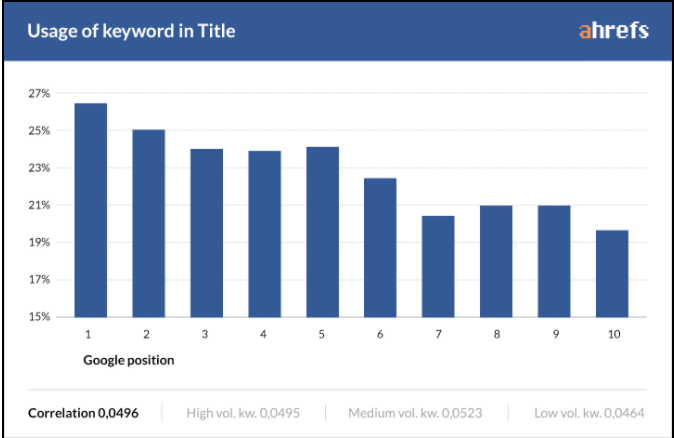
The truth: A title tag, however unsexy, plays a critical role in search engine rankings, click-through rates, traffic volume, and search engine optimization (SEO) success.
Get titles wrong, and you risk rankings and traffic. Get titles right, and not only will you improve your rankings, but you’ll improve your bottom line.
In this article, we’ll explore every facet of title tags: what they do, how they work, why they're important, what makes a good title tag and a bad title tag, and how they impact your SEO.
We’ll even layup a step-by-step guide to crafting and optimizing click-worthy, SEO-friendly title tags.
Sit down. Buckle up. Let’s go!
Get brand new SEO strategies straight to your inbox every week. 23,739 people already are!Sign Me Up
What is a title tag?
A title tag is an HTML element that defines the name of a webpage. Simple and brief, but important. After all, the title of a page tells potential visitors what they can expect to discover. And search engines use page titles as a ranking factor when ranking websites. Which means title tags should be both descriptive and persuasive.
A page’s title appears in four key places across the web:
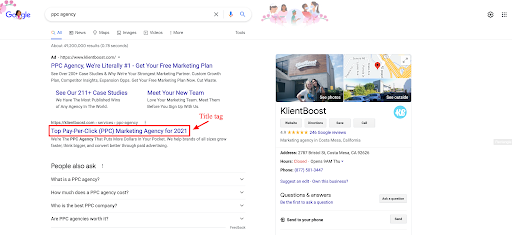
1. Title tag in SERP snippet
The title of a page is the most prominent feature of a SERP (search engine results page) snippet (below), and search engines generate titles from the title tag on the page. On Google, titles appear in big, blue letters.
2. Title tag in browser tab
Page titles also appear within each open tab in your browser. Hard to notice when you have dozens of tabs open, but they serve as navigational cues to help visitors move from tab to tab quickly.
3. Title tags in social media, text message, and messenger links
Your title tag also determines what appears when you share a link on social media, via text message, or through a messenger app. While Facebook open graph markup allows you to create unique title tags just for FB, by default, the title within a snippet is generated by your title tag.
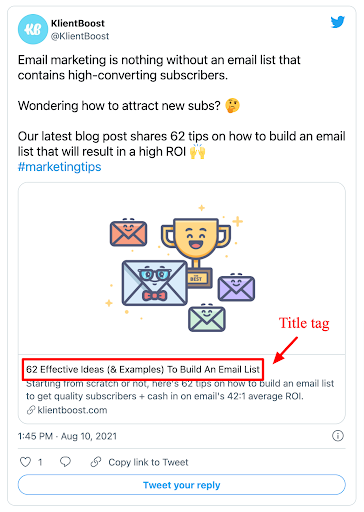

4. Title tag in bookmarks tabs
Last, title tags populate the titles of bookmarks in your browser. So when you forget who or what you bookmarked but know you bookmarked it, you can sift through titles to find the right page.
Title tag examples
Title tags come in all shapes and sizes: short, long, branded, non-branded, descriptive, persuasive, or both.
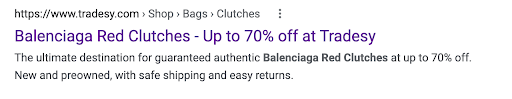
Ecommerce product page title tag
Descriptive. Brand name. Offer included.
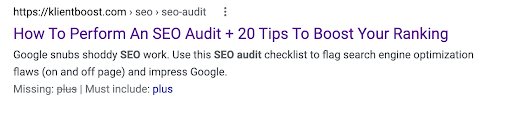
Blog post title tag
Enticing with a value proposition.
Local business title tag
County name. Benefit (“emergency plumbing”). Brand name.
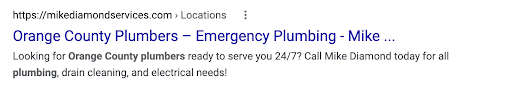
Directory title tag
Specific. Regional. Brand name.
Emoji title tag
Google supports emojis, unless they’re inappropriate.

Benefits of title tags for SEO
Why are title tags important to search engines and SEO? Rankings and click-throughs.
Ranking factor
Search engines have come a long way since the boolean days of the late 90s. But even Google still uses keywords in page titles as one of their 200+ ranking factors.
In fact, Moz ranks keywords in title tags as the second most important on-page SEO factor. And mountains of data show that pages with keywords in their title tag rank higher.
Click-through rates
Then there are click-through rates (CTR).
Click-through rate refers to the number of clicks a search result receives out of the total number of queries. For example, if 100 people type in “donut shop” and the first result receives 75 clicks, then that website's click-through rate is 75%.
What do CTRs have to do with title tags? More enticing title tags = Higher CTRs = More website traffic.
But is CTR a ranking factor?
There’s a debate in the SEO industry regarding CTRs in search results and whether or not they influence rankings.
Moz has conducted studies that suggest click-through rates do influence rankings (Google has even spoken about the importance of click data indirectly). But when questioned, Google has adamantly denied it.
Here’s why it doesn’t matter either way: Even if click-through rates don’t matter to Google, they should matter to you or your SEO, since capturing a higher volume of total search queries is the name of the game.
Ranking factor or not, optimizing your title tags is the easiest way to increase click-throughs to your website and improve your SEO.
How to optimize your title tags for SEO
Page titles are like first impressions. Let’s explore seven ways to optimize your title tags so they’re click-worthy and seo-friendly.
1. Write page titles for people first, search engines second
First, use natural language and syntax. Make title tags readable and for people above all.
Next, understand the context of the search. Every page is different. Navigational? Informational? Transactional? Time-sensitive? Something else? Depending on the context, what you include will vary.
Last, understand the intent of the search. At this point, hopefully you’ve already researched user intent and let those insights inform your website content. What is the core outcome a searcher intends on achieving by clicking? Put it in the title. Every page is different.
Let’s explore a few title tags with different intent and context.
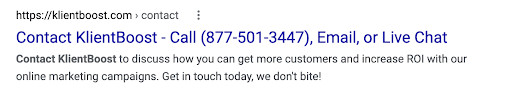
Contact page
If someone is searching for your contact page, they intend on contacting you. Include a number, and let them know the different ways they can contact you if they click.
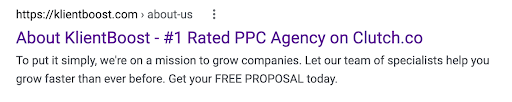
About page
If someone searches for “your name + about,” place a relevant award or accolade in the title of your about page to prime them before they click.
Reviews page
If someone searches for reviews about your business, and you have a page to rank for “business name + reviews,” include the number of reviews or star rating in your title tag.

2. Use main keyword(s) in title tag
According to Moz, research and experimentation continues to see lower correlation between on-page keyword use (like keywords in title tags) and rankings. Likely because Google’s RankBrain algorithm continues to get better at understanding the meaning of a page without relying on keyword phrases.
Brian Dean found the same results: Though keywords in title tags seem to be a definitive “ticket to entry” to get you on page one, once you’re there, using the exact keyword doesn’t seem to help you climb any higher.
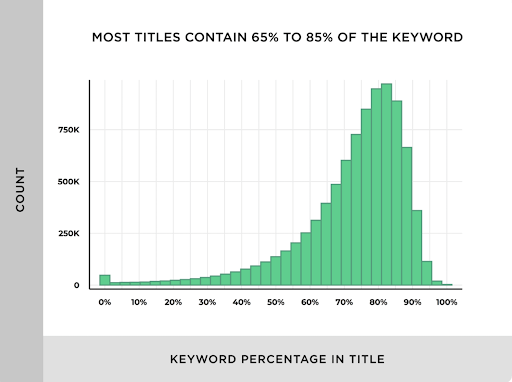
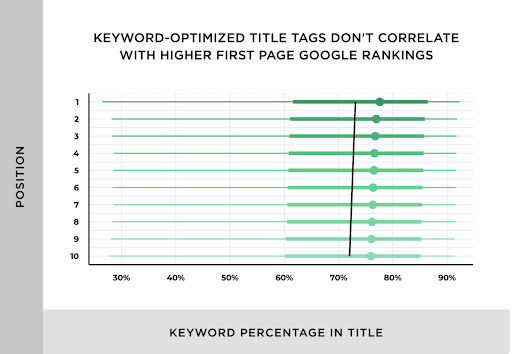
Bottom line: It’s a good idea to include your target keywords in your title tag. Google still uses keywords in title tags as a ranking factor, even if it’s declining. And it benefits the user anyways.
Also, Nielsen reported that many visitors scan as few as the first two words of the title. And keywords closer to the start of the title may have more of an impact on rankings. So consider frontloading your keywords early in the title.
3. But don’t stuff your title tags with keywords
Don’t spam your title tags with keywords in hopes they’ll increase rankings. They won’t. It’s bad for the user and readability, and it could get you in trouble with Google. One keyword will do, or a second variation of the keyword if necessary.
Avoid keyword stuffing
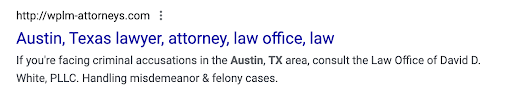
From Google: “Avoid keywords stuffing. It's sometimes helpful to have a few descriptive terms in the title, but there's no reason to have the same words or phrases appear multiple times. A title like "Foobar, foo bar, foobars, foo bars" doesn't help the user, and this kind of keyword stuffing can make your results look spammy to Google and to users.”
4. Keep title tag length concise, but don’t overthink it
How long should a title tag be? It depends on who you ask.
Most SEOs recommend keeping title tags between 50-60 characters (600 pixels). Anything longer and Google will truncate (hide) portions of the title since they can only fit a maximum of 60ish characters in a snippet.
But according to Gary Illys, Google’s webmaster trends analyst, Google doesn't have a recommended title tag length; it’s an “externally made-up metric”:
“Try to keep it precise to the page, but I would not think too much about how long it is and whether it’s long enough or way too long.
If it fills up your screen, then probably it’s too long, but if it's just one sentence that fits on one line or two lines, you’re not going to get a manual action for it.”
So do longer title tags have an SEO benefit?
When asked if there’s any value to having title tags that are longer than the displayable space of the snippet, Gary replied with, “Yes.”
So what do we recommend?
Like Gary says, don’t overthink it. If you can make your title tags descriptive and concise, then do it. Somewhere between 50-60 characters will ensure the entire title tag appears in search results.
If your title tag extends beyond 60 characters, expect that portions of it may get cut off in search results.
But if you need more than 60 characters to clearly articulate the page’s title to Google, then stick with it.
5. Make page titles unique (don’t duplicate title tags)
Each page needs its own distinct, descriptive title. Don’t use the same title tag for more than one page. And don’t use vague titles like “Home” or “Products.”
From Google: Titling every page on a commerce site "Cheap products for sale", for example, makes it impossible for users to distinguish how one page differs fom another. Long titles that vary by only a single piece of information ("boilerplate" titles) are also bad; for example, a standardized title like "<band name> - See videos, lyrics, posters, albums, reviews and concerts" contains a lot of uninformative text. One solution is to dynamically update the title to better reflect the actual content of the page: for example, include the words "video", "lyrics", etc., only if that particular page contains video or lyrics. Another option is to just use "<band name>" as a concise title and use the meta description (see below) to describe your site's content.
6. Brand your title tags when it makes sense
Brand recognition matters.
In a study from years ago, SearchEngineLand discovered that nearly 70% of consumers look for a “known retailer” when deciding which result to click on.
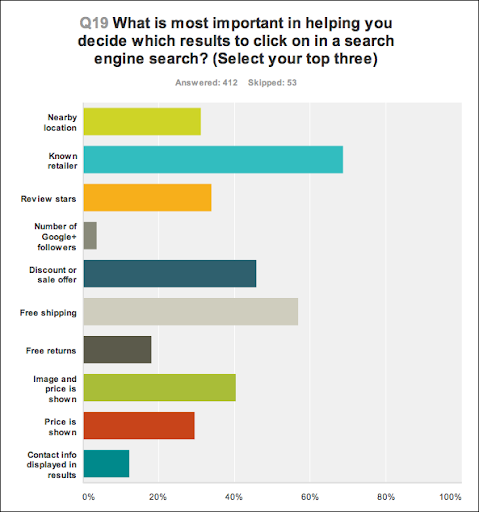
Makes sense. How many times have you clicked a search result in position 5, 6 or 7 because you were more familiar with their brand than the ones that preceded it? All the time.
Rule of thumb: Brand your title tags on a page-by-page basis. And only brand them as long as your brand name doesn’t occupy valuable space that could better be used to make the title more descriptive, relevant, and, thus, more enticing.
As your brand grows stronger, your branded title tags will convert more and more search queries to clicks.
7. Sweeten the deal with a value proposition
Click. Through. Rates. Entice clicks by adding value propositions to your titles.
Ask yourself: What’s in it for the reader? Don’t dance around the promised land. Tell your visitors how they’ll benefit from clicking, directly from the title. Visitors online want one thing: to accomplish something. Give them a goal worth pursuing.
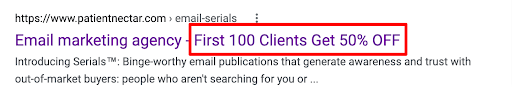
Discount
They’re looking to buy. Let them know you have lower prices.
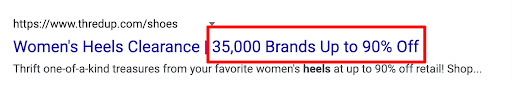
Benefit (Real-world data)
They want insights. Let them know yours are evidence-based.
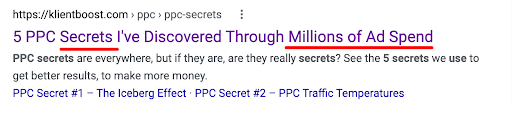
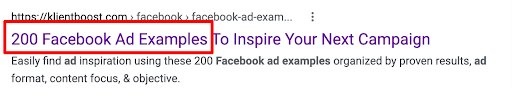
Benefit (Most examples)
They want ad examples. Let them know you have more than anyone else.
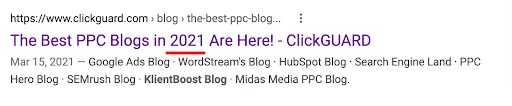
Benefit (Most current)
They want the most current. Let them know yours is updated.
Promise
They want to learn. Let them know what they’ll take away.
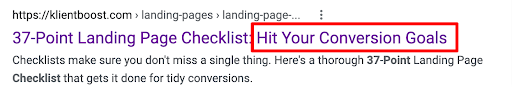
Offer
They’re shopping for products or services. Prime them with an offer they can’t resist.
Why is Google rewriting my title tags?
Google reserves the right to generate a new and improved title tag if they think they can make it more descriptive, distinct, relevant, and easier for the user to understand.
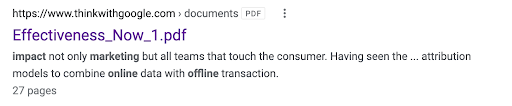
How? By sourcing alternate text from anchors, meta descriptions, page content, and “other sources.” Let’s look at an example from Google itself:
Actual title tag on the page
Rewritten title tag in SERPS
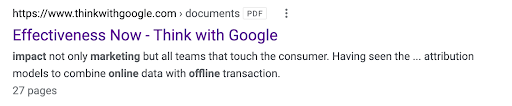
In a recent study from Moz, they discovered that 58% of tracked URLs with title tags were rewritten by Google. Some 7,000 of those “rewrites” were merely truncated. But even still, that’s a lot of rewritten title tags.
To ensure yours gets rewritten less often, make sure to follow the seven steps for optimizing title tags from above.
Tools to help you write better title tags
Since you’re reading this article, chances are you haven’t optimized your title tags yet.
Here are some SEO tools to help you out:
- Google SERP simulator: See exactly what your title tag will look like as it does on Google
- Yoast SEO plugin for WP: Easily update title tags within WordPress
- CoSchedule’s headline tool: Get your page title graded for free
- Atom.io: HTML editor to edit title tags manually
- w3schools: Practice editing title tags for yourself in their HTML editor
- Clearscope.io: A tool that helps you quickly optimize for important keywords and user intent
Title tag FAQ
What’s the difference between a title tag and an H1 tag?
<h1> to <h6> are HTML tags used to define headings on pages. <h1> is most important; <h6> is least important.
Title tags and H1 tags serve a similar purpose: they both describe the main subject of the page.
However, whereas title tags appear in the aforementioned places above (SERPS, shared link snippets, bookmarks, browser tab), H1 tags only appear on the page.
Title tag
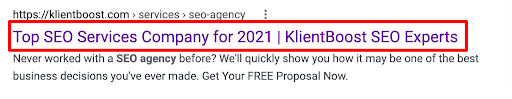
H1 tag
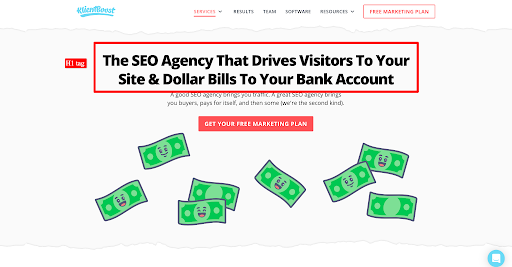
What’s the difference between a title tag and a meta description tag?
The meta description is the short description that appears below the title in search snippets. It adds additional information about the page, but it’s controlled by the <meta name=”description” content=”insert description here”> html tag, not the title tag.

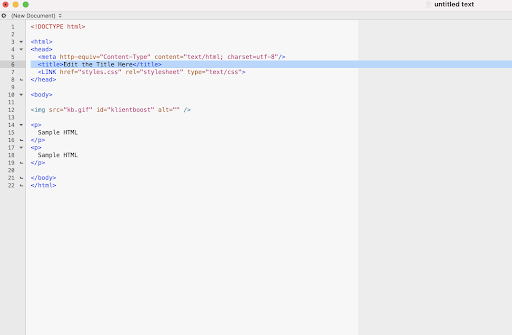
What does a title tag look like in HTML?
The <title> tag is a required element found within the <head> tag at the top of every HTML document. In the past, your title tag had to be text-only. But now, search engines like Google support emojis (though they may filter them out).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Top SEO Agency for 2021 - KlientBoost SEO Experts</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The SEO Agency That Drives Visitors to Your Site & Dollar Bills to Your Bank Account</h1>
<p>A good SEO agency brings you traffic. A great SEO agency brings you buyers, pays for itself, and then some (we’re the second kid.</p>
</body>
</html>
How do I change the title tag?
Rest assured, every major content management system (CMS) like Wordpress (Yoast or All in One plugin), Wix, Squarespace, Drupal or Spotify will allow you to change the title tag from the page’s editor without needing to dive into HTML code.
If you don’t use a CMS, you can change your title tag by opening up a page’s HTML document using a text editor and doing it manually.
What next?
Think of title tags or page titles like mini advertisements: Your page title makes a promise about what’s on the other end of a click. A promise to search engines. A promise to potential visitors.
Botch the title tag and risk losing rankings and traffic. Get it right, and not only will it improve rankings, but it will improve your bottom line.
What next? Start optimizing. And start testing title tags.