Need to generate more sales for your online store? Or even bring more foot traffic to your brick and mortar? To achieve this, you need to boost the visibility of your products.
What better way to do so than to meet consumers where they are? At home.
There are over 6.8 billion searches on Google daily. And many are shopping for products like yours. You can put your products front and center (or top) of their search results by using Google Shopping ads.
This means more folks coming to your site (or store) and buying your goods.
But effective campaigns require the proper structure, optimization, and tools to generate results.
In this guide, I’ll explain how to use Google Shopping Ads to grow your store's sales. So let’s take a look.
- What are Google Shopping ads?
- Google Shopping ads benefits
- How effective are Google Shopping ads?
- What is Google Shopping & how does it work?
- How to set up a Google Shopping campaign
- Google ad annotations & labels
- Google Shopping ads best practices
- Setting goals for your Google Shopping ads budget
- How do I choose keywords for Google Shopping ads?
- What are Google Shopping Actions?
- Google Shopping Ads FAQs
- Start building your Shopping ad campaign
Get brand new Google ad strategies straight to your inbox every week. 23,739 people already are!
What are Google Shopping ads?
Google Shopping ads allow merchants to promote their products on the search results page of Google Search. These ads appear when users perform searches that include specific keywords or phrases related to the product being promoted.
For example, if you sell shoes online, you can create a Google ad with the keyword "kids shoes" in it. When someone performs a search for "kids shoes," your ad will appear at the top of organic listings.
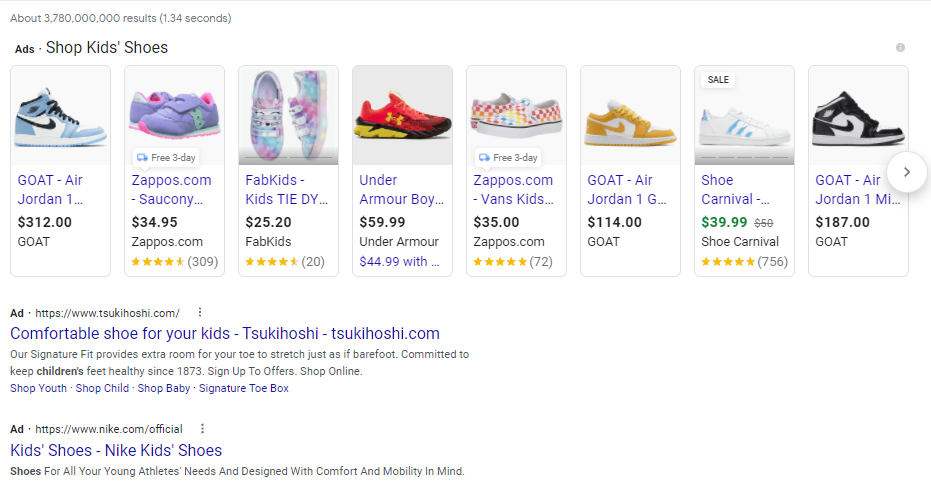
Of course, this would be nearly impossible to rank for since the keyword is so broad. But more on keyword selection later.
When you click on the "Shopping" tab at the top of Google search, it'll take you here:
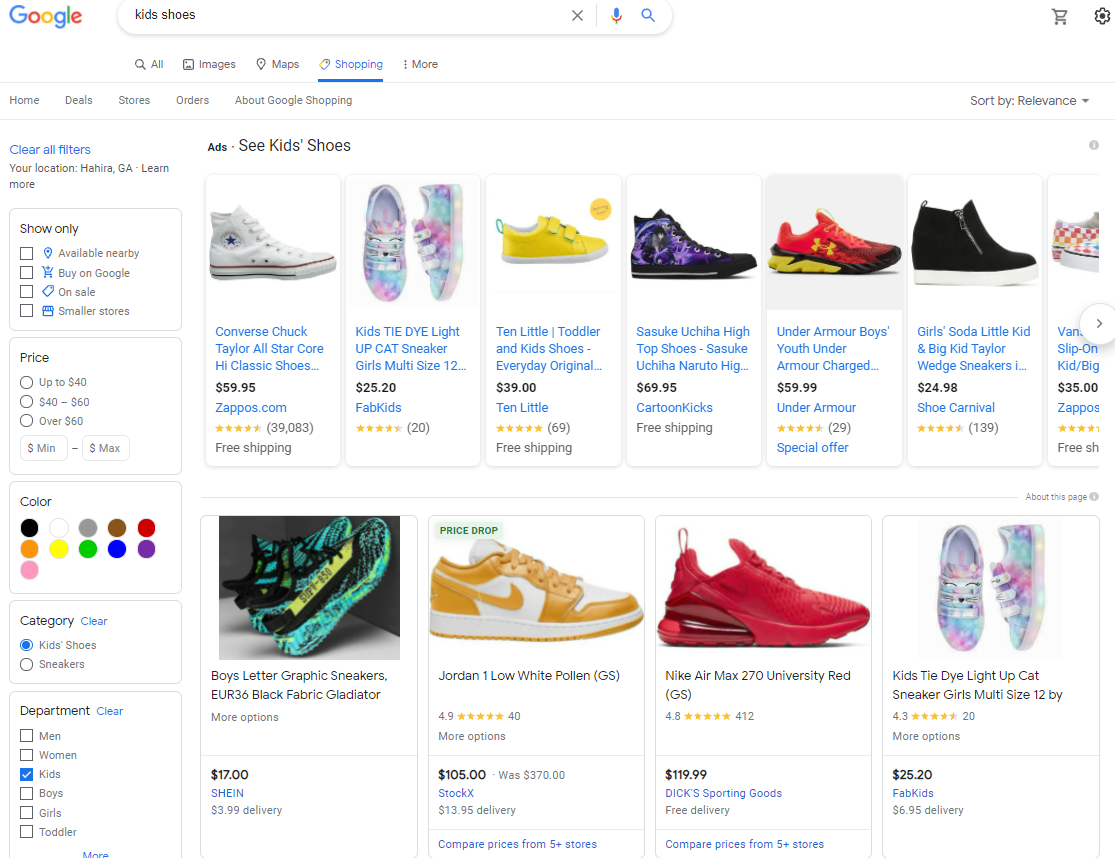
Each product listing ad includes the brand name/URL, ad copy, price, and annotations (i.e., Free Shipping, In stock, etc.).
Below the ads, you'll find products published to Google Shopping. E-commerce shop owners across the US, Latin America, Europe, and Asia can list products for free on Google Shopping.
Google Shopping ads vs. Google search ads
Google's sole priority is to deliver results to searchers that best suit their intent. So if it believes the query is transactional (the user is looking to buy), then it’ll display Google Shopping ads and listings.
“Google Ads are the lifeline for any online business, but even more for e-commerce brands. While Google Ads operates as a shotgun approach to advertising by trying to hit the widest group, Google Shopping is a more concentrated (rifle) approach. This is because with Google Shopping, you are hitting the exact person who is searching for your product. They already know what they want, and your product being the search result is their answer.” — Peter Cuderman, Owner of Sandi Lake Clothing.
When you search for dresses in Google, you see Google Shopping ads (as images in the carousel at the top). And Google search ads at the bottom (all text).
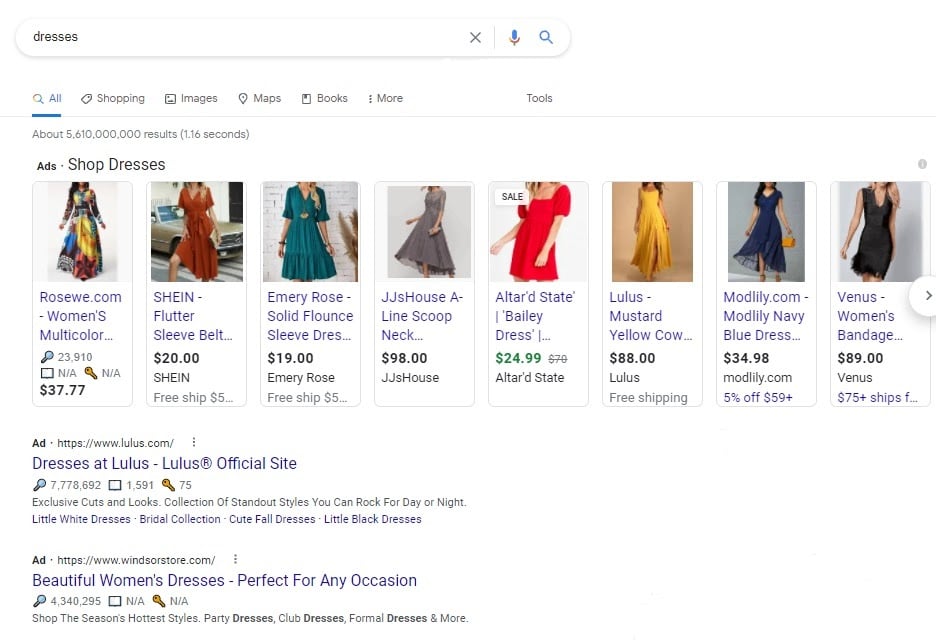
Which would you click on as a consumer?
Odds are, it's the photos of the dresses. This is what makes Google Shopping ads a better option for e-commerce store owners than text ads.
What are Google Smart Shopping campaigns?
Standard Shopping ads are one way to grow your online sales. But there's another way to promote your products using Google Smart Shopping campaigns. This allows e-commerce sellers to broaden their reach by displaying their ads across Google's various networks:
- Google search (and shopping tab)
- YouTube
- Gmail
- Google display network
Google Smart Shopping campaigns work by automatically optimizing your ad placement (and bidding) to maximize conversions for your online store (based on your budget). It'll even use machine learning to pull from your product feed and test variations of text and product images to show relevant ads to users.
These campaigns feature three types of ads:
- Product shopping ads
- Local inventory ads
- Display ads
This gives you more opportunities to experiment with your advertisements and see what converts best. Sportline, an Argentinian sporting goods retailer, saw 227% increased conversion value and 621% return on ad spend (ROAS) when using this approach.
Google Shopping ads benefits
There are many reasons why eCommerce businesses should use Google Shopping ads. For example, it helps to:
- Increase conversions: People performing a product search are ready to buy. If your Google Shopping ad appears at the top of the search results, it has a high chance of receiving a click. Not only does this boost your click-through rate (CTR), it increases the odds of a conversion
- Improve SEO: Google Shopping ads appear at "position 0" (above the #1 URL in the search results), and it shows before the text Google ads. This makes them a powerful SEO tool, which helps capture leads from organic searches
- Boost brand awareness: Advertising does one thing well—build awareness for brands. The more people see it, the more they'll remember your business. Then when it comes time to purchase, they may go directly to your site to buy
- Increase your reach: There are only 10 positions on the first page of Google. Competing with other brands for the top spot is challenging, especially if you have low domain authority (DA). With ads, you can skip to the front of the line (as long as you properly optimize them and outbid your competitors)
- Improve lead quality: When a user clicks on an ad, their intention is to purchase. They're in or near the last stage of the funnel and are ready to buy. This improves the quality of the traffic coming to your online store
- Learn more about your customers: The analytics alone is enough to make Google Shopping advertising worth it. You can learn about who's clicking on your ads, which products perform the best, and how your ad campaigns compare to competitors
How effective are Google Shopping ads?
It depends on your industry, ad spend, and optimization skills. But based on research from Sidecar, the average click-through rate for Google Shopping listings is 0.84%.
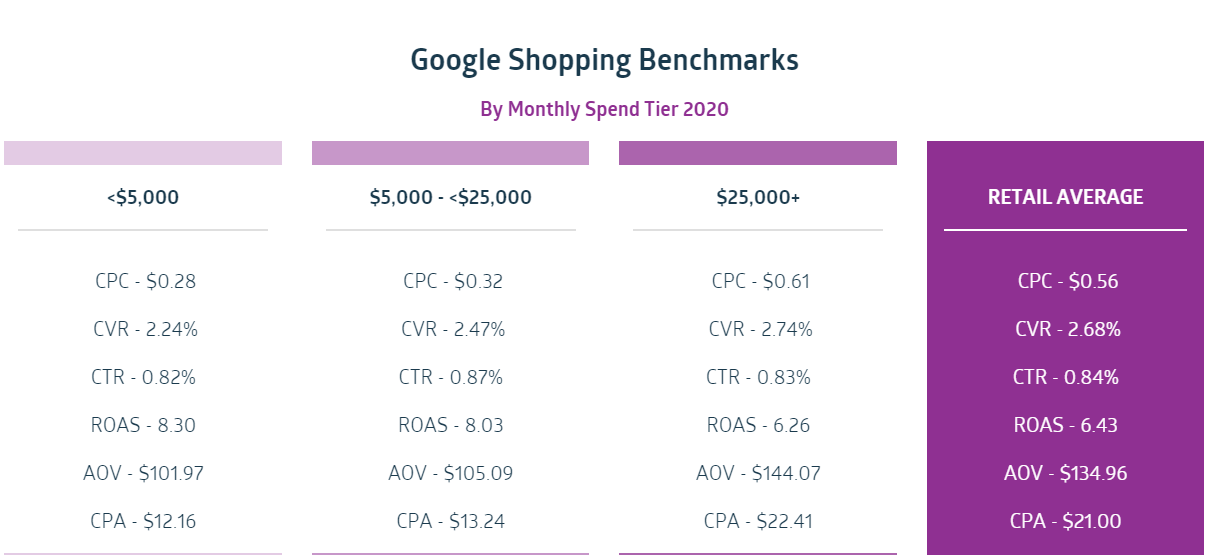
And the average Google Shopping ROAS is $6.43 (per $1 spent). These are excellent returns on investment, which is why more businesses are investing in them.
Google Shopping ads cost
The cost of your Google Shopping ad campaigns depends on the keywords you bid on. It can sit anywhere from a few cents to a few dollars (or more). On average, we find Shopping ad cost-per-click (CPC) is $0.56.
How much you spend daily depends on you. For example, you can start with as little as $5 per day. This is the limit you set—once reached, Google pulls your ads down. You can also choose which days you want your ads to run and your monthly spending limit.
“My method for scaling up the Google Shopping ads has always been to increase after viewing results for at least two months. After that, I will scale up or down accordingly. After changing any spending setting, I will again wait two months to use it as a benchmark for success.” — Peter Cuderman
Monthly budgets for Google Shopping vary by industry. Some spend hundreds of dollars, while others spend thousands.
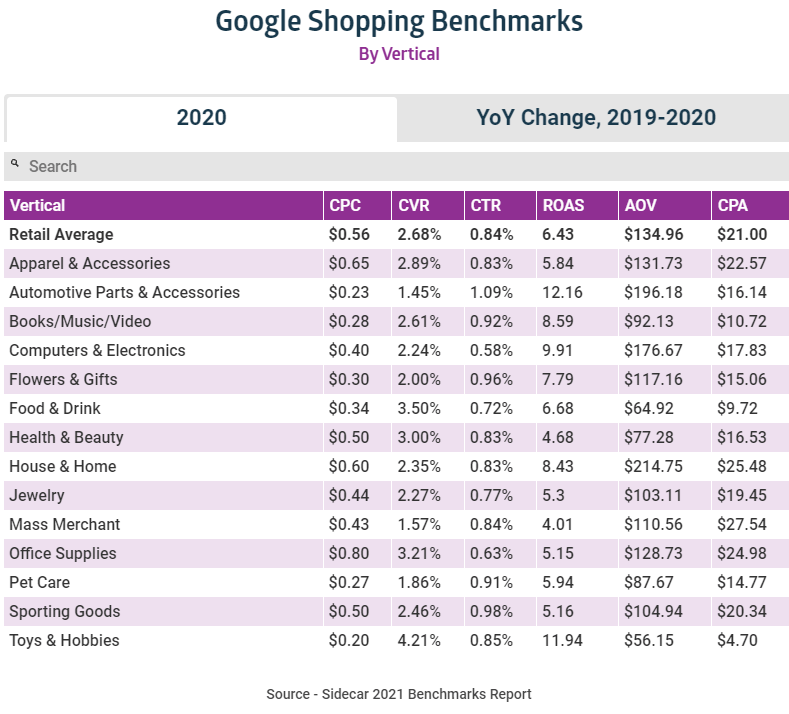
Learning what others are spending on Shopping ads in your vertical will give a clue of what to spend on your own ad campaigns.
What is Google Shopping & how does it work?
Google Shopping is a platform eCommerce sellers use to display their products to buyers. Google ads are the method eCommerce businesses use to promote their products to prospective customers. Both work together to help increase traffic to websites.
Type in a product into Google search. At the top of your SERP, you'll find a carousel of products you can browse through. If you select the "Shopping" tab at the top, it’ll take you to Google's shopping platform.
Here, you'll find a wide selection of the products you searched for. You can use the search bar at the top to search for other or similar products to improve the search results.
You can think of it like Google search, but for products only.
Google uses a unique algorithm for Google Shopping ads (compared to regular search ads). It pulls results from your store's product feed, including its title, description, price, reviews/ratings, and product image.
It takes product details, matches them with relevant search queries, displaying them as ads in the search results.
Does Google Shopping work with Shopify?
Yes, you can add products on your Shopify store to Google Shopping. When you create a new listing using Shopify’s built-in storefront, you have the option to add Google Shopping as part of your ad group.
You can also use the Google Channel app to promote your products using Smart Shopping campaigns.
How to set up a Google Shopping campaign
Setting up a Google Shopping campaign is simple and free. All you need is a Google Merchant Center account, and you can begin adding your products and building campaigns. Here's a look at the steps:
- Create a free account
- Add your products
- Include detailed product information
- Set up campaigns
- Optimize your landing page
- Promote your site
- Measure success
- Improve performance
- Scale your campaigns
Once you're all set up, begin experimenting with your Google Shopping campaign. A/B testing is an excellent way to find what works for your products.
Google ad annotations & labels
Adding annotations and labels to your ads can grab attention and increase clicks. There are several types to choose from—those that indicate a sale or price drop. Or to highlight your shipping or return policy.
Here's an example of how ad annotations look:
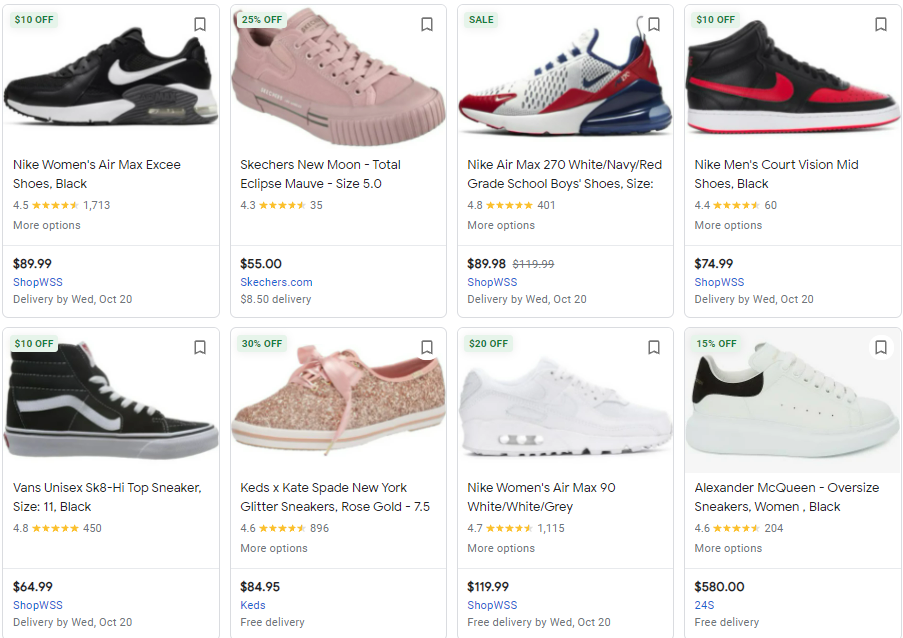
At the top of these products, you can see words like "$20 Off" and "30% Off." It can also show annotations like "Great Pick" or "Curbside” to entice clicks.
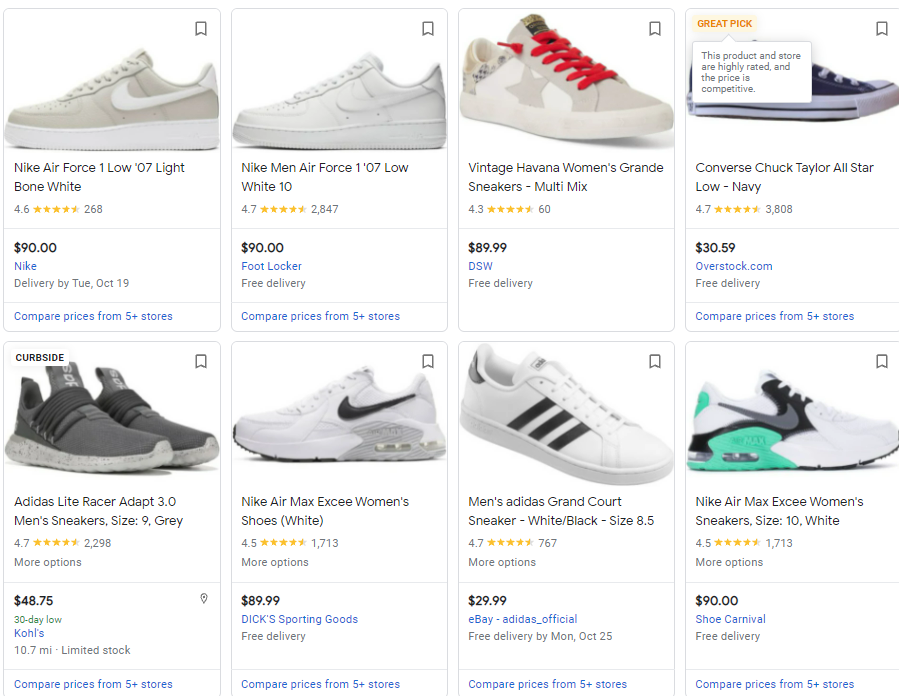
Other annotations you can use:
- Shipping policies (i.e., Free 3-day delivery)
- Return policies (i.e., Lifetime returns)
- Local inventory (i.e., Available for pickup today)
- Reviews (star rating and number of reviews)
- Buy on Google (i.e., Add to cart)
But how does using Google ad extensions and annotations improve your rank? In the chart below, you can see the impact they have on your ad's position:
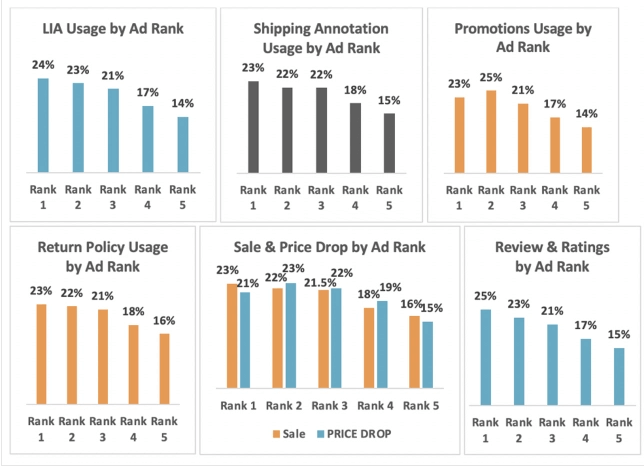
It appears most top-ranking ads use ad extension and annotations. The lower the usage, the lower the ranking.
Google Shopping ads best practices
Your Shopping ad campaigns puts your products in front of potential shoppers. But you need to use the right strategies to get optimal results. Here's a look at what other e-commerce businesses are doing to boost their conversion rate and sales.
Use keywords that match searcher intent
When selecting keywords for your ad campaigns, make sure it matches the intent of potential customers. Using the wrong keywords can lead to wasting ad spend on non-performing product listing ads (PLAs).
For example, it's better to use long-tail keywords. "Shoes" is a broad term and doesn't signify buying intent. So instead, you can add key phrases like "white dress shoes for weddings" (if it has search volume).
Remove unprofitable ads
Not all ads will yield favorable results, so consistently weed out and remove the low performers. This will allow you to reinvest those dollars into the ads with higher conversions.
But how do you identify the "losers" in your ad campaigns?
There are two types of losers.
- The ones that are getting you a ton of traffic, but no conversions and
- the ones that get you a ton of really, really expensive conversions.
To find the first type, customize columns to mirror the structure of your campaign and add in columns for product details such as product type, brand, etc. For each group of products look at the costs. Filter through the products to find the losers.
To find the second type you have to know your profit margin first. Once you know the profit margin, scan through your bids. Any that exceed your profit margin can be labeled a loser. Change your bids once you know your winners and losers.
Use high-quality photos
Images can increase click-through rates and improve user experience. So make sure to choose high-quality images for feature photos to promote clicks. Be sure to include multiple product pictures from different angles to your product listing. Use a high-resolution camera and proper lighting to make them more appealing.
Also, consider using unique photos vs. stock images, especially if you're in a competitive industry that commonly uses stock photography. You can make your product listing ad stand out by having human models, different backgrounds, and props.
Use negative keywords
Getting a lot of ad clicks doesn’t mean much if the folks aren’t buying your products. High traffic with poor conversion rates not only hurt your sales, but eats away at your advertising budget.
“Take advantage of the negative keywords function. This feature makes it so you don’t appear for given keywords. It can be helpful because it can cut out a lot of the traffic that land on your page accidentally.” — Chelsea Cohen, Co-Founder of SoStocked.
Optimize product titles
Your title tag is an essential element of your ad’s optimization. And it plays a role in whether people buy your product. Product titles need to have enough detail to entice shoppers to click and contain keywords your target audience will search for.
For example, if you sell men's clothing, try using words such as: "Men's Dress Shirt" or "Tuxedo Shirts.” Or if you sell women's dresses, try using words like: "Women's Evening Dresses" or "Black Party Gowns.”
Set up remarketing lists
Remarketing lets you reach people who've visited your site before. They were interested enough to click through your website. But something happened and the visitor left before making a purchase.
You can potentially bring them back using ad retargeting.
“Retargeting is a gem when it comes to optimizing ads. Retargeting is a strategy where your ads are shown to people who are familiar with your brand. They’ve either previously visited your website or interacted with your page. Research shows retargeted users are 70% more likely to convert into customers compared to cold audiences. Following the most successful tricks is the best way of scaling ads. This includes using Lookalike audiences, reusing your most popular ads, avoiding audience overlaps, and slowly increasing your ad budgets.” — Yana Trihub, UX scientist at KeyUA.
Create ad groups for a strong campaign structure
Ad groups provide a granular view of your campaigns. It helps you see where there might be room for improvement. Plus, it gives you insight into whether some products perform well across various audiences. You can view product data by going into your Google ads account.
For example, you can have an ad group for various types of jewelry, such as rings, bracelets, and necklaces. Then break it down further into men’s bracelets, rings, and necklaces. You can continue subdividing each ad group to give you that granular view for product ad performance.
Another option is to use Single Product Ad Groups. This allows you to zone in on how each product performs. For example, you can see which keywords each product ad group triggers and how much they earn. With these insights, you can decide which to boost or drop from the campaign.
Setting goals for your Google Shopping ads budget
Set realistic expectations about how much money you want to earn monthly per channel. If you don't know your daily, weekly, or monthly conversions, it’s impossible to gauge success.
For instance, let's say you run an online shoe shop. The average conversion rate is 1%. That means that out of 100 visitors, only 10 become buyers. But if you sell shoes for $100, you'd need to generate $1,000 worth of revenue just to break even. In other words, you would need to attract 2,500 shoppers to turn a profit.
Use your Google ads analytics to track data and gain valuable insights into your performance. It's also a good idea to track your outranking share.
“Using target outranking share analysis, you can determine your position in the market and invest accordingly. This can also help in the formation of future strategies and hence, stand out in the market.” — Nathan Watson Lion Locs
What is target ROAS (return on ad spend ROAS)?
This is an ROI metric measuring the amount of money spent in relation to the value gained from your ads. For example, if you invest $5,000 in advertising but end up generating $10,000 in sales, your ROAS will be $2 (per $1 spent).
Here's the formula you can use to calculate ROAS:
Revenue from ad conversions / Total cost for ad = ROAS
An ideal ROAS depends on your industry, products, competition, and season. You'll have to analyze your particular market to determine comparable ROAS and then use that as a benchmark to set realistic goals.
How do I choose keywords for Google Shopping ads?
The keywords you use determine the results you'll get. But how do you remove the guesswork? One option is to monitor the keywords your customers use to find you.
“One of the biggest tips I can give when managing Google Shopping Ads is monitoring the products you submit and the keywords that trigger your ads. Sometimes we see that a certain product takes up a majority of our budget, but results in no sales.
Look at the keywords triggering that product in Google search. If they're unqualified keywords, add those as negative keywords, and monitor the results. If the keywords are on target, then consider removing the product from the feed so your budget can go to more profitable products. Implementing this strategy has saved us a ton of money over the years and helped us increase sales.” — Jeff Moriarty, Marketing Manager at Moriarty's Gem Art.
Another way to remove the guesswork is to partner with a digital marketing agency, specializing in SEO and Google ads. This backs your campaign with data and experience vs. relying solely on intuition.
What are Google Shopping Actions?
Google Shopping Actions is a program merchants use to display their products across Google's platforms. This way, shoppers can find and purchase their items using mobile, desktop, and voice assistant.
Its purpose is to create a seamless shopping experience by providing consumers with a:
- Shareable list
- Universal shopping cart
- Instant checkout
- Saved payment credentials (digital wallet)
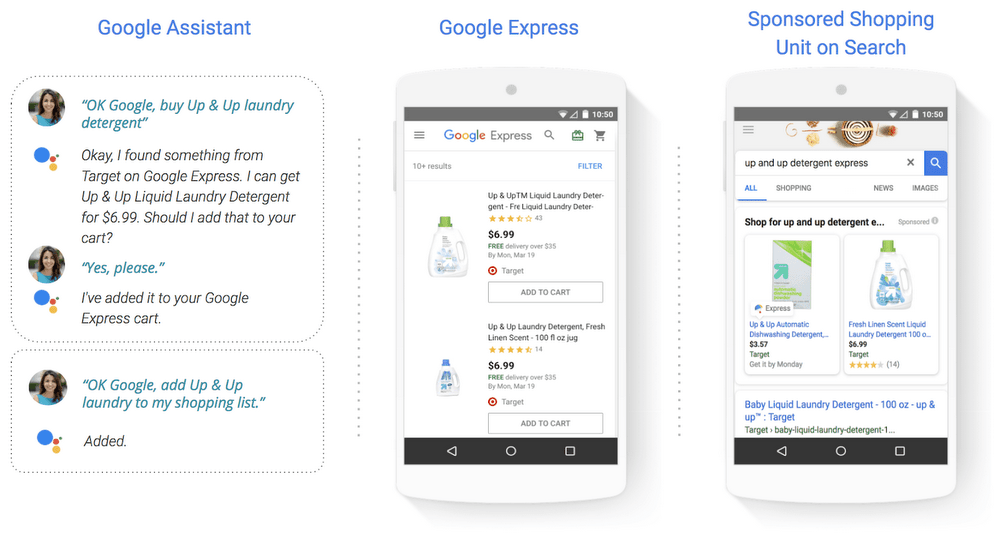
This allows customers to easily turn a search into a purchase no matter the device (or Google platform) they're using.
Google Shopping Ads FAQs
Why are my Google Shopping ads not spending?
There could be several reasons why your campaigns aren’t performing well. Here are some common ones:
Your bid amount may be too high or low compared to competitors.
You might need to adjust your bids based on seasonal trends. For instance, if there was a big sale during Black Friday, you would want to raise your pricing accordingly.
If you don’t know where to start, try adjusting your bids first before trying other strategies.
How does bidding work in Google Shopping ads?
Bidding refers to setting a price per click. You set your maximum daily cost per conversion, determining how many times someone will view your ad each day. Then, you choose whether to pay CPM (cost per thousand impressions) or CPC.
How long does it take to get impressions and clicks in Google Shopping Ads Listings?
It depends on the number of products listed, but it takes about two to three days for your ads to show in the shopping feed. Once the ads are visible, you can receive impressions and clicks immediately.
Start building your Shopping ad campaign
In this guide, you learned what Google Shopping ads are, how they work, and how to use them to grow your e-commerce sales. The next step is to start building your own Shopping ad campaign.
Remember, your campaigns are experiments, so don’t be afraid to test different strategies. Maybe a different photo, ad copy, or promotion will yield better results.
But if you’re not ready to dive into an ad campaign, then we have more great tips for you. Check out how to set up your Google Merchant feed to start using Google Shopping and learn more about improving your online sales.