“What gets measured gets improved.“ — Peter Drucker
Admittedly, our man Peter wasn’t talking about SEO specifically, but tracking SEO results is necessary if you want to know the complete story.
Keeping track of your website traffic alone isn’t worth much. You also want to know your keyboard rankings, critical SEO metrics, and improve overall SEO performance.
With an effective SEO tracking system in place, you can objectively identify what’s working with your campaign and optimize what isn’t.
But how does all this work? Only one way to find out… keep reading.
Get brand new SEO strategies straight to your inbox every week. 23,739 people already are!Sign Me Up
What is SEO tracking?
SEO tracking is a critical aspect of evaluating your campaign’s success. You use it to measure the progress and performance of your campaigns.
Generally, you should establish your SEO strategy before starting campaigns. Consider these questions to avoid missteps:
- What is your company history and what do you do?
- What's the monetary value of a qualified lead?
- What are your most profitable products or offerings?
Next, define which SEO metrics you’re going to track, how often you’re going to be reviewing them, and how you want to report the performance to clients. Try to set campaign goals that are measurable, specific, and shareable.
How to measure and track your SEO success?
To set yourself up for SEO success, you have to establish your end goal and then design your entire SEO campaign around it. Once you do that, you can focus on tracking and measuring results to direct your SEO efforts.
Tracking SEO performance and results
Wondering how to determine whether your SEO strategy is effective and if you have a good average position? Answer: By monitoring important SEO KPIs.
The thing is, there are hundreds of metrics (we kid you not) to track. Case in point: Google alone uses 200 ranking factors in its algorithm.
You obviously cannot track them all, so it's better to monitor key metrics that matter most for your business. Read on as we discuss some popular KPIs to measure your SEO results.
1. Organic traffic
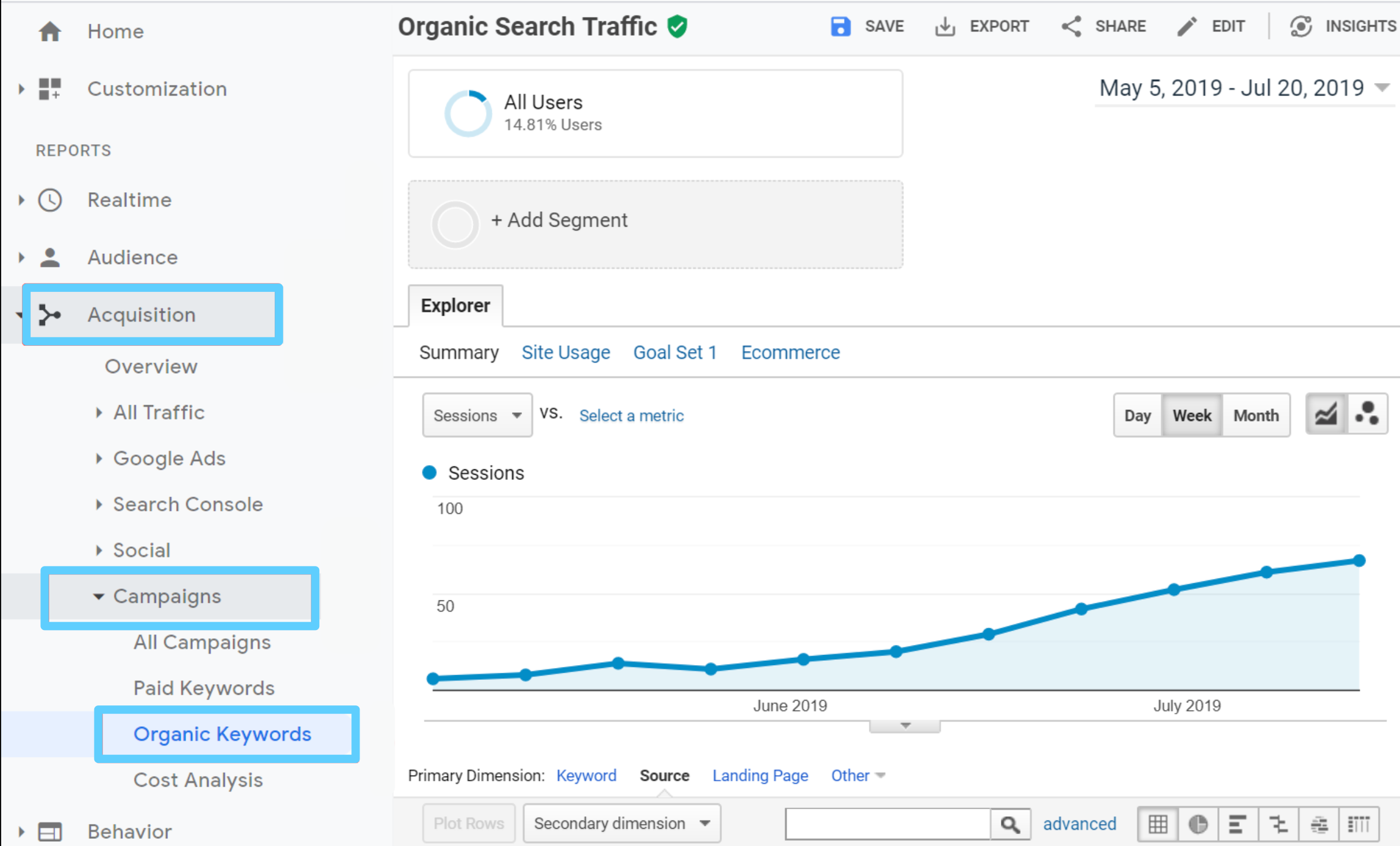
This KPI measures the number of visitors that visit your website through organic search results. Its growth indicates you’ve reached your main SEO objective of getting more people to come to your website.
Organic search traffic comprises targeted individuals looking for something specific. If you can provide them with a solution, you’ve got yourself a paying customer.
2. Search rankings
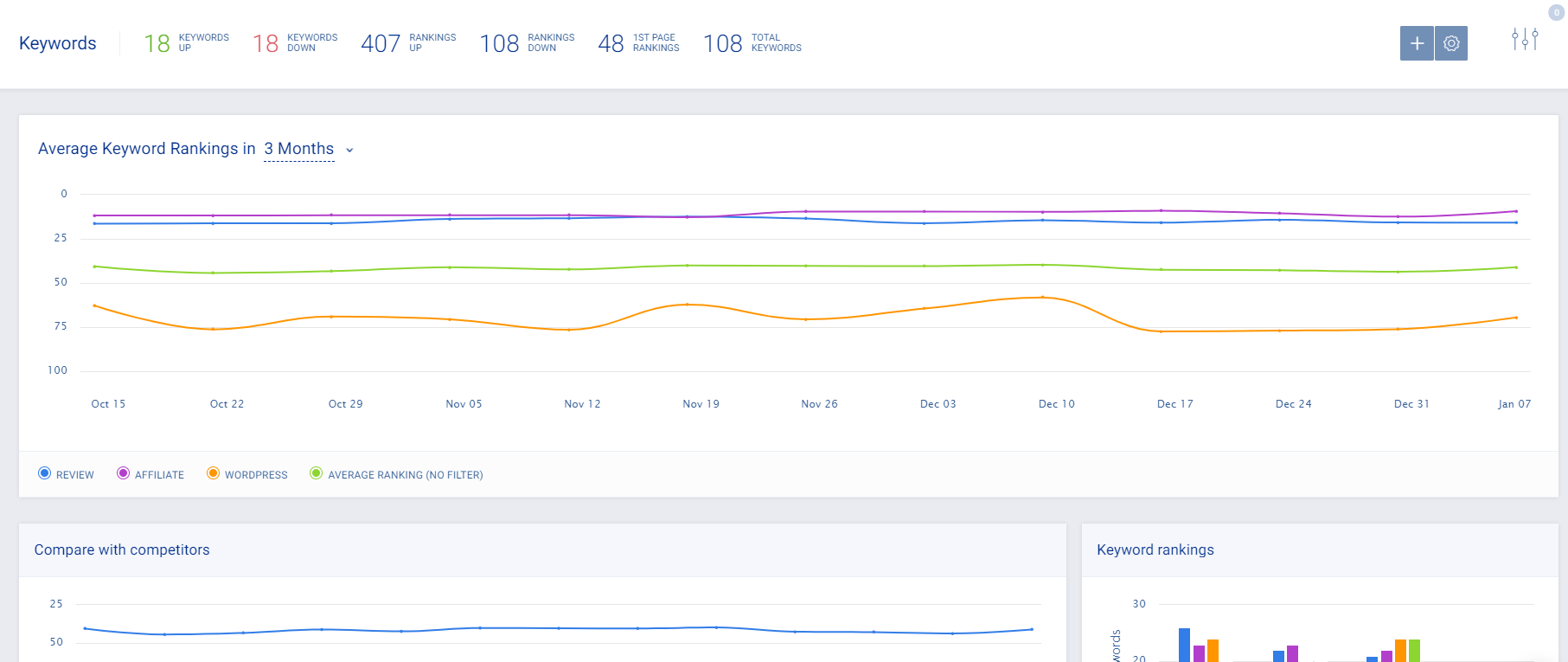
Ranking for keywords is one of the most important premises of SEO. The higher your website ranks for the relevant keywords, the better your traffic, leads, and conversions.
It’s also important to track rankings for the right keywords. For example, if your website's ‘Shirts‘ section ranks in the first place for the ‘Red and blue striped shirt,’ your website traffic won’t improve much. Your ultimate goal is to get on the first page — or as close to the precious first spot on Google as possible.
3. Search engine visibility
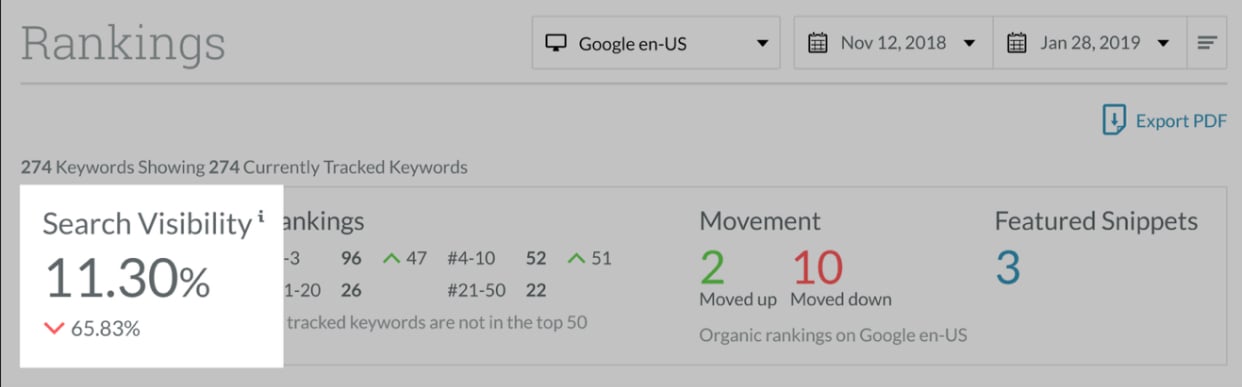
Whenever a user pops up a query on Google, the search engine produces an outcome or a search engine results page (SERP). The result includes a cocktail of organic results, paid ads, and SERP features, such as featured snippets, image packs, and knowledge panels.
Search engine visibility indicates how often your domain is shown in the search results. Basically, it gives you a birds-eye view of your overall SEO progress and search volume.
4. Competitor analysis
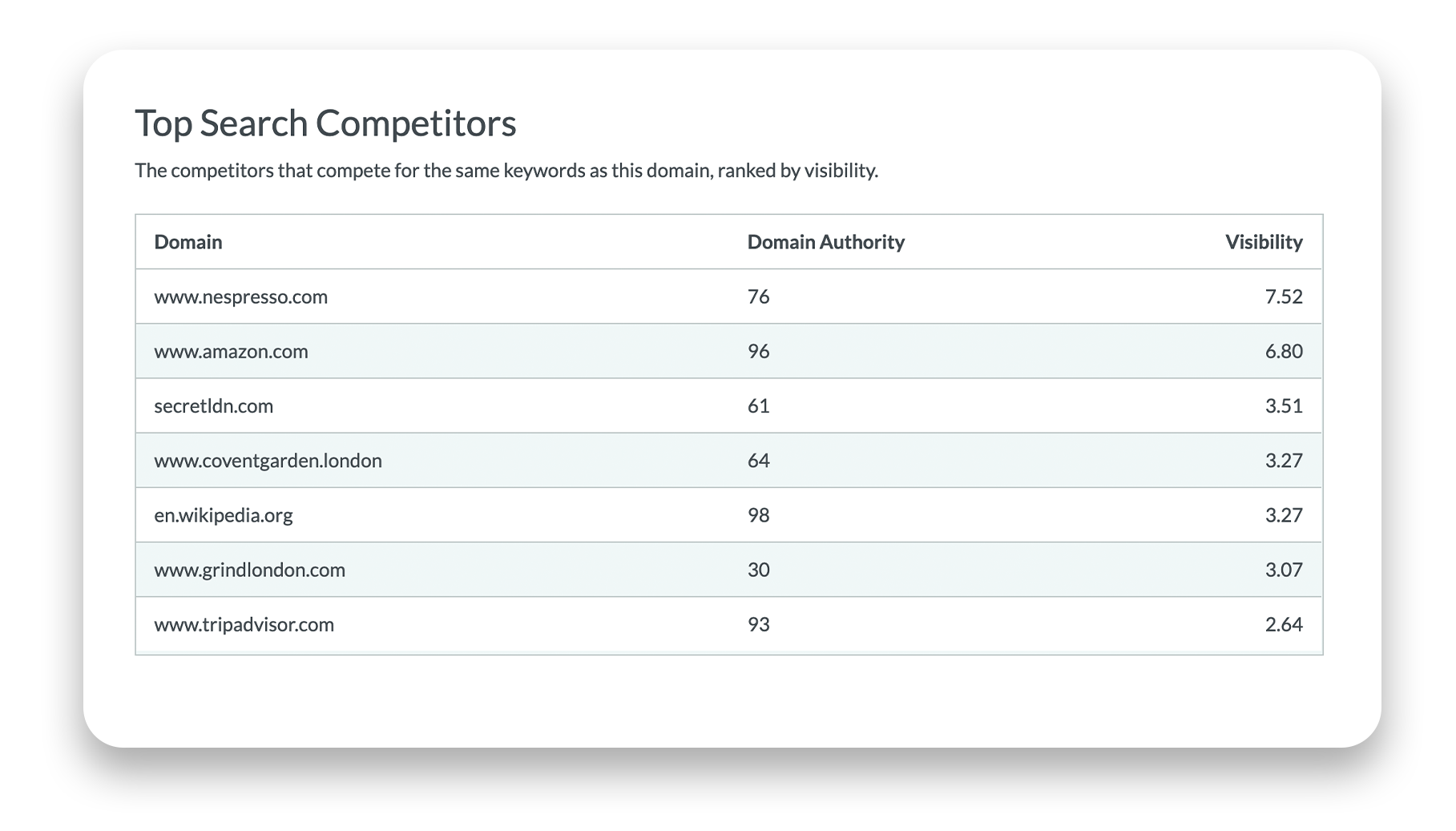
In addition to your own metrics, you should also keep track of your competitors to identify new opportunities to enhance your SEO campaigns. Track your competitor’s keywords, their domain authority, and other SEO metrics you think will help you refine your campaigns.
Besides the above metrics, you should know your website’s overall clicks and impressions, which indicate the total number of Google users that click on your website in search results and the number of users that saw your site rank for a specific keyword, respectively.
In the end, the whole point of SEO is to sell more.
If you want to determine just how successful your SEO campaign was, take a look at your total sitewide conversions. Besides Google, you can also find out how many new customer leads are coming from different search engines like Bing and Yahoo.
Measuring SEO health
After tracking SEO comes measuring SEO.
Although you don’t have to include the health of your website in SEO reports, it’s required to facilitate effective website optimization.
Examples of measuring your SEO health include:
- Indexable pages
- Structured data
- XML sitemap errors
- Number of web pages not receiving traffic
- Number of web pages with errors
To measure and track your SEO effectively, we’ve created an SEO metrics guide that covers the ten most critical metrics in detail.
What are the best SEO tools for SEO tracking?
In this section, we’ll discuss a few SEO tools that do an excellent job at maximizing your SEO efforts. You can also check out our in-depth SEO tools guide to learn our top picks for all things SEO.
Before we begin, you should know there are many different tools, such as our favorites Moz, Ahrefs, Semrush, and Sitebulb, that let you track your site’s position in SERPs, do site audits and link building, among other tasks. But we find that leveraging your search engines’ own tools really helps uncover SEO opportunities, as well as identify (and eliminate) potential issues.
- Google Search Console: Google Search Console (GSC) provides actionable reports to help detect website errors and opportunities, as well as improve user engagement
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Bing Webmaster Tools and Google Search Console are similar tools offering the same functionality. You can use Bing's Webmaster Tools to determine how your website is performing in Bing and surface improvement opportunities
- Lighthouse: Lighthouse is Google‘s automated tool to accurately measure a website‘s performance, progressive web apps, accessibility, and more. Using this data, you can better understand how to improve your website performance, achieve a specific speed, and access valuable insights
- Structured Data Testing Tool: This tool validates that a website is using schema markup, also known as structured data, properly
- PageSpeed Insights: This tool gives you website performance insights using Lighthouse and Chrome User Experience Report data derived from real user measurement (RUM) when available
- Rank Tracker: Rank Tracker is designed to provide additional information on top of what you see in GSC, including competitive insights, SERP feature tracking, and improved tracking to help you rank on Google’s first page
Tips for tracking SEO results using Google Analytics
For effective SEO tracking, you need to measure three critical metrics:
- Unbiased search engine rankings
- Website traffic from search engines
- Website conversions from search engine traffic
We’ll show you how you can use Google Analytics to monitor all three metrics in a single place and improve the effectiveness of your SEO campaigns.
1. Unbiased keyword rankings
Google uses many factors like previous browsing history, the type of device you’re using, and the user’s geographical location to personalize search results. This also makes it harder to manually check your website rankings.
In such cases, you can use your free Google Analytics data along with a rank tracking tool like RankRanger. Here’s how this works:
- Collect your rankings data in Google Analytics and link your account to Google Webmaster Tools. Read this guide for instructions.
- Go to Acquisition > Search Console > Queries to view all keywords your website is ranking for.
- Check how many impressions and clicks your website has, as well as its average position in Google and average CTR.

You now have access to all data to see how edits to your website affect your SEO over a specific time period. That said, don’t make rankings your sole priority — they aren’t your end goal. You also want to track your traffic and conversions.
2. Website traffic from search engines
To see data related to your website traffic, you’ll be working with Google Analytics’s Acquisition feature.
- Click Acquisition on the side menu bar.

- Go to All Traffic > Channels.
- Select organic search channel in the report table.
You should now see all the organic or non-paid traffic visiting your website from different search engines. Focus on analyzing the trend of the graph spanning over 6-12 months, and not get too caught up with the exact numbers.
Is the graph going upward or downward? This will tell you how your SEO campaigns are performing over time.
3. Website conversions from search engine traffic
Rankings and website traffic don’t equal sales, which makes conversions from search engine traffic an extremely crucial metric to monitor. Luckily, Google Analytics allows you to measure all of the conversions directly from your SEO efforts. Here’s how to go about this:
- Set up Analytics Goals. You can read this guide for more information.
- Return to the same Channels report to view all goals from organic search traffic.
- Monitor and measure your conversions.
If you have an e-commerce website, the instructions are a bit different. Do this instead:
- Set up E-commerce Analytics to keep track of the exact revenue generated from your search engine traffic
- Change the Channels report from Summary to E-Commerce in the Explorer navigation (this will be above the graph) to see your total revenue from organic search traffic.
Google Analytics custom reporting feature simplifies the entire SEO process further.
3 effective strategies for SEO tracking across all stages of the conversion funnel
According to experts, a good conversion rate is between 2% and 5%. But getting a jump of even 0.5% can be a big deal, which is why all efforts — big or small — matter and can impact your campaign’s success.
When companies start their SEO campaign, they generally follow this methodology:
- What keywords are best for my business?
- How can I rank on the first page of a search engine for those keywords?
- How do I optimize further and find more keywords to increase our rank and domain authority?
After figuring out the answers, their next step is to develop an SEO strategy that involves identifying content to write based on the appropriate keywords. Then companies try to get backlinks and social shares for their content to achieve their end goal, whether it’s to generate more leads or boost conversions.
While this certainly makes sense, there's so much more to talk about and perhaps even make the approach more cost-effective.
Below, we’ll walk you through how to map your target audience's keywords to segments and funnel stages to simplify evaluating how many leads and how much traffic you can generate in each of these areas.
Create a list of topics you want to cover at the higher level
Similar to how a strong foundation keeps a building standing, understanding what topics to cover will make your SEO strategy more effective.
Topics can be anything that appeals to your audience. You can have very business case-specific features that go “here is the problem, here is my solution.“ Or you can create pieces centered around people’s work that covers what your customer does on a given day and how you can help make their work more efficient.
Your business. Your call.
Another approach would be to cover topics around specific tools or processes that are valuable for your customers. For example, you can cover broad topics like digital marketing automation, demand generation, and content marketing strategies, as well as sub-topics on automation tools like Salesforce, Marketo, and lead scoring and grading.
When deciding topics, always remember you should be able to link them directly to your offering. If you are a product company, choose topics specific to one of your products. If you are a services company that offers digital marketing services, you should write content about digital marketing.
Do you see where we're going with it?
Build out your spreadsheet
Once you’ve decided on your topic, you need to choose keywords for each of your topics and categorize them. Things get pretty interesting as you start collecting data on average monthly search engine volume and potential click-throughs and conversion rates.
To monitor user intent, go to Google Search Console and take a look at your metrics. If you see you can get up to 500,000 impressions for the keywords at the top of your sales funnel stages, and you’re only getting 300,000 impressions, you know you need more backlinks and content mapping and have to work on optimizing specific pages — or even build new ones.
This will help you model and forecast how much traffic you could generate, how many leads you could get from the traffic, and then potentially uncover how many opportunities you could generate based on that data.
Organize keywords based on marketing funnel stages and website placement
All keywords are not created equal.
Some keywords are searched when users are still trying to learn about a specific topic (top of the funnel); some search terms are more specific to evaluate different vendors or solutions (middle of the funnel/bottom of the funnel).
That’s why your next step is to segment keywords further based on two factors:
- Where they are in the funnel
- Average monthly search volume to maximize traffic
You can also sort out your keywords by considering how much traffic you can get based on the topic. Then split it further down by segmenting based on final placement and getting more granular by evaluating topics and final stages by location. We particularly recommend this if you’re targeting certain markets or cities.
Another tactic we find works well is categorizing keywords by landing pages on your website. You may not do this immediately, but it can be an effective long-term strategy to map out your SEO content effectively moving forward.
SEO tracking = Better SEO campaigns
Tracking and measuring SEO is an essential aspect of the search engine optimization process.
You can use it to gauge whether your strategy is working, whether you’re achieving the results you desire and understand where and how you can improve moving forward.
Having tools like Google Analytics and Search Control make the ride even easier.
We hope this guide will help you understand how your SEO efforts impact your business, as well as identify ways to meet your goals.
