Doing keyword research, link building, improving site speed, making high-quality content, blah blah blah.
You already know the basics of search engine optimization (SEO), but you need more.
Don’t get me wrong—all that is great advice. But from where you’re currently standing, you’re still not ranking #1 on the search engine results.
Clearly, something isn’t working.
SEO isn’t a siloed practice anymore. It has transformed into a prominent revenue channel and is quickly being integrated into content marketing practices and elaborate digital marketing strategies to ensure better outcomes.
You have to stay on top of the ever-evolving search engine landscape and make sure you‘re applying optimization techniques correctly.
To give you a fighting chance at minimizing technical issues and maximizing website performance, here’s a comprehensive guide to help you avoid the most common SEO mistakes.
- 1. applying SEO tips without a viable game plan
- 2. not understanding your audience and their search intent
- 3. shallow understanding of the nuances of comprehensive keyword research
- 4. forgetting that slow sites don’t win the SEO race
- 5. producing the wrong type of content
- 6. ignoring SEO analytics
- 7. disregarding the inevitable mobile-first future
- 8. using external and internal links poorly
- 9. not using title tags,meta descriptions, or schema
- 10. making headings too short or too long—and not using them right
- 11. writing ordinary or plagiarized content
- Avoid common few mistakes to rank better
Get brand new SEO strategies straight to your inbox every week. 23,739 people already are!Sign Me Up
1. applying SEO tips without a viable game plan
Imagine you set out on a road trip without a map or GPS. You can have the adventure of your life, but it’s rather unlikely. You can make the wrong turn, take the longer road, end up circling the same area—so many things can go wrong.
The same holds true when it comes to SEO.
If you want your content to pop up as search query answers, you need a good SEO game plan. You cannot hit your lofty goals, whether it’s increasing sales, boosting conversions, or ranking higher on Google if you don't optimize your web content based on SEO best practices.
Despite this, a shocking 70% of small businesses don’t have an SEO strategy. If you’re a part of this statistic, you need to shift gears and come up with a competitive advantage that makes it easier for you to rank—or arrive at your intended destination.
The solution:
Thorough planning can make any road trip successful. Using the same logic, you can improve your SEO game by taking inventory and gauging your competitors and their metrics—rankings, keywords, content, and performance.
Study your key competitors’ strategies and refine your SEO strategy. Try to target overlapping customer bases, keywords, and other types of content that are unique to your brand. These efforts can help your site rank higher with the SERPs.
Also, be open to using automated technologies to improve workflow and optimize processes.
2. not understanding your audience and their search intent
Having a granular understanding of your target audience is a fundamental SEO principle.
Many SEO experts think they know their audience, but the reality is different. They don’t know how customers in their industry behave or like and dislike—nor do they understand their search intent.
All your efforts should be guided to help the search algorithm connect the customer to the most relevant, accurate, and up-to-date information.
You get this right, and you win Google.
The solution:
Channel your SEO efforts towards funneling your target audience down the specific channel you want them to go to. Put out content that answers their search intent and provides value to them, irrespective of whether they are in the market to buy, sell, learn, or invest.
You should also analyze macro trends to understand your niche market.
Find out how a visitor would search for or refer to your product or service, and put forth a plan of action accordingly. For instance, some search engines and users prefer long-tail keywords that are more specific and longer than short-tail keywords.
Take advantage of both historical and real-time data to identify changes in customer behavior over the years. You can use the insights to guide your SEO strategy and keyword selections.
I found a lot of success using Google keyword research tools and vendor tools. Highly recommend giving it a shot.
3. shallow understanding of the nuances of comprehensive keyword research
Keywords, keywords, keywords.
Businesses make tons of mistakes when it comes to choosing, adding, and managing keywords. These mistakes can have some serious consequences. So you might want to pay a little extra attention here.
The first mistake is using unoptimized keywords or the wrong keywords. This refers to instances when the content isn’t used in agreement with the selected keywords.
Search engines rank content based on whether the keywords are being used in the content enough times in relation to the chosen keywords. So there is a high chance your content may rank poorly in terms of search engines.
The second mistake is assuming long-tail keywords would bring in less traffic.
Using long-tail keywords is actually a great idea to improve your site’s SEO value. Yes, these types of keywords have a lower search volume, but they can be very specific to your business and help draw in your target customers.
The third mistake is targeting high-traffic keywords solely.
Marketers and content writers give greater importance to high-volume keywords thinking this approach will help them bring more traffic to the site. This tactic can work, but only if your site has a higher DA. It definitely won't when you have a relatively new website.
Better to use keyword research tools like Semrush that will tell you exactly how competitive a specific keyword is and give you a super useful list of high-traffic to low-traffic keyword suggestions to incorporate.
The solution:
Try to introduce the keyword phrase early on in your content, albeit organically. My advice would be to use it in the first paragraph of your content, whenever possible.
When selecting keywords, choose a balanced cocktail of long-tail and short-tail keywords and high-traffic keywords. Avoid making assumptions without data to back them up, and try to add keywords that will have a positive impact on your overall conversion rate.
You don’t want to neglect branded keywords, too.
Your content should be focused on your targeted audience and their search experience. When you include branded keywords, you can target people searching for branded queries that represent your customers—or very likely future customers.
Also, while you try hitting the minimum keyword count, don’t go overboard.
Keyword stuffing used to be the bread-and-butter of early SEO, but search engines have since adapted and now prefer content with natural language patterns. Today, the priority is to write content for people first and search engines second.
4. forgetting that slow sites don’t win the SEO race
Your site speed is a huge, huge factor when it comes to SEO.
Slow websites can cost you hard-earned SEO traffic. All the time and effort you invested in optimizing your website will become futile if your page takes too long to load.
But wait a minute, is your website actually slow?
Run a quick test on Google PageSpeed Insights to find out. This amazing tool from Google itself lets you check your site speed within seconds and provides an overview of the different areas you can improve to boost the speed of a specific page.
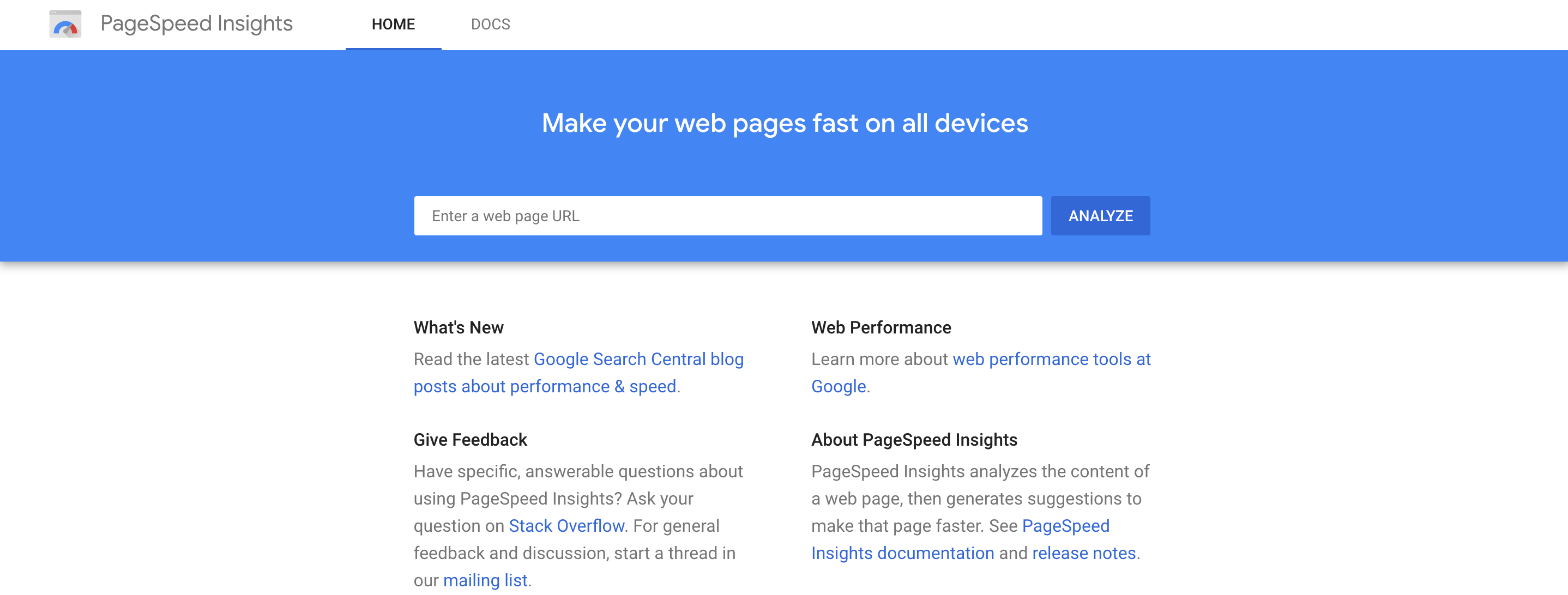
Google recommends a page load time under two seconds. But the faster your site, the more people are likely to stay on it and the more Google will favor it.
The solution:
Several factors can delay your page load time. All you have to do is identify and fix them, and you’ll have a super-fast site in no time.
Optimizing your images can be a good start. Many websites have a lot of images, which take longer to load, and hence, slow down the page load time.
Your best bet is to resize your images by setting the ideal image size to 72dpi. Install a WordPress plugin (if you have a WordPress website), use a picture editing tool, or experiment with different image formats like JPEG 2000 and WebP to reduce the bandwidth used by your images.
Additionally, you can compress JavaScript and CSS code by using shorter names for variables and do a site audit of all internal URLs to identify the reason behind redirects and fix them. Both methods can significantly improve site speed.
5. producing the wrong type of content
Marketers don’t always focus on creating content for the right audience. That’s strike one.
While ranking for a particular keyword is the end goal, this shouldn’t be at the cost of producing content that’s not relevant to your audience. Publishing articles that aren't focused on your targeted topics will only jeopardize your SEO campaign.
If marketers do produce relevant content, they don’t base it on expertise and make it authoritative and trustworthy. That’s strike two.
Your primary objective should be to produce content that corresponds authentically to your target audience’s needs and questions. It should also include the right search terms to help search engines trace your content and match it with the keyword you’re optimizing for.
The solution:
Focus your energy on creating content that Google wants—relevant, accurate, and optimized for keywords.
Similar to Google, other search engines also want to serve users with the most relevant content for their search queries. The better your content answers the queries, the higher it’ll be in the search rankings.
Based on my experience, here are a few tips to produce the right type of content:
Include keywords where it makes sense. Too many keywords is synonymous with low-quality content.
Don’t fit different topics within a single piece of content. Keep your piece simple and to the point.
Optimize for multiple keywords in a single article. Less isn’t always more when it comes to SEO, but don’t go overboard.
Only publish content that directly answers questions your target audience is searching for.
Experiment with different types of content for different needs and SERP layouts, such as visuals, video, and text.
Another good tip is to follow Google’s best practices on E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) and search quality. Basically, you want to align your content with effective SEO strategies, as decided in your game plan.
6. ignoring SEO analytics
SEO isn’t only about driving organic traffic—it’s also about converting this traffic into sales. Unfortunately, many marketers disregard numbers, which is where they commit their next SEO mistake.
SEO tracking is necessary to know if your SEO and content efforts are genuinely working. For instance, you may be wasting your time hyper-focusing on high-traffic keywords when you could get better conversion rates by optimizing for low-traffic keywords because of their specificity.
There is no cookie-cutter SEO strategy. Make sure you regularly track and analyze numbers to get the necessary information to make sound decisions.
The solution:
Use reliable tools, such as Google Analytics and Google Search Console to measure and get an overview of your website’s performance. These will help you determine just how effective your current optimization strategy is for different kinds of content and decide for yourself whether you need to make any changes.
Besides the above, you should be open to trying out other SEO tools and platforms. Today, the SEO technology space offers some amazing tools—both free and paid—for various causes, such as:
- Keyword research
- Competitive analysis
- SEO management and workflow
- Link management, reporting, and measurement
- Automation
When choosing tools for your website, consider the following questions:
- How well does the tool or platform serve you and your organizational needs?
- Can the tool help implement your SEO strategy without shooting up your budget?
- Considering the higher price point, does the SEO platform meet the maximum of your requirements? Are there any alternatives that offer more?
- Can the tool or platform increase efficiency and execute your SEO content strategy seamlessly?
7. disregarding the inevitable mobile-first future
We’re living in a mobile-first world now.
Search engines can recognize when your website isn’t optimized for mobile devices, especially Google since it places a lot of emphasis on mobile-first indexing. Moreover, mobile search accounts for over 50% of all web traffic. But despite the facts, many businesses still rely on outdated web designs that haven’t been optimized to deliver a seamless mobile experience.
Some of the biggest SEO mistakes that marketers make on mobile are:
- Slow website speeds
- A non-responsive web design
- A difficult navigation system
- Slow video and picture loading time
- Missing or incorrect local information
If any of these sounds familiar, no points for guessing what should be next on your to-do list.
The solution:
As Google moves towards a mobile-first search index, you should simply follow its lead.
But before that, you must ensure your site’s HTML code complies with Google’s AMP guidelines to avoid potential damage to your site performance. Check for invalid AMP pages on your site with a Site Audit tool. This will help you identify areas that need fixing.
Next, improve your website’s loading times to prevent mobile users from bouncing off your page. You can consider a website redesign too—one that uses a responsive cross-platform setup—to make it easier for users to browse your mobile site.
Producing content aimed at giving users a better mobile experience can also create a happier customer base and help keep them on your site for longer. Eventually, these prolonged interactions will increase your SEO ranking and help drive revenue.
8. using external and internal links poorly
Amateur marketers believe adding several external links to your content will help them make the most from SEO.
It won’t.
More than the number of external links, it’s the quality of the links that matters. It’s why you don’t want to add links from just any site. Instead, link your article to relevant, higher-ranked websites with a higher domain authority (DA).
Linking back to sites that have been linked to you can also be useful. This will bring back traffic in the future, helping you score better with the search engines.
Another mistake here includes going astray with internal links.
When publishing content, you should consider your top-performing pages and try to place those links in your content. This will give your own content more visibility and create additional traction.
However, don’t include internal links just for the sake of having them in an article. If they don’t match the topic, don’t add it.
Another counter-productive link-building practice is using ineffective anchor text.
Anchor text indicates to the search bots and the reader what the link is about and how it can help users. If you have ineffective anchor text for quality links, it’ll only lead to wasted precious SEO opportunities.
The solution:
Develop a link-building program based on quality linking and best practices. Also, in no circumstances should you engage in buying links. It won’t bode well.
In the case of internal linking, try to balance the number of internal links to use and avoid linking to irrelevant pages. You can try grouping topically-related web pages with internal links, as well as conduct an internal link audit to identify and fix broken links, slow pages, and differentiate important versus unimportant non-important pages.
Consider building your content onproven content creation principles.
When you publish great content, you'll attract quality links by default. Using technologies and tools to regularly monitor and check for broken links and fix them, as well as build new ones can also be useful.
As for anchor texts, avoid using generic phrases like “click here.” I recommend experimenting with different anchor texts for your content. Using the same phrases repeatedly can be seen as spammy.
9. not using title tags,meta descriptions, or schema
After adding the relevant keywords to your article, you must write optimized title tags and meta descriptions.
Search engines consider both of these factors when crawling your website, so skipping them is not an option. Yes, meta descriptions aren't a ranking factor, but they do influence your click-through-rate (CTR).
Another SEO mistake content marketers make is forgetting to use schema to mark up their content and inform search engines what their website is all about.
Without schema, search engines will struggle to understand context, leading to a lower ranking. This holds true even if you have a lot of high-quality content on your website. Your web pages will also be less relevant to specific queries made through voice search.
The solution:
Don’t rush your title tags and meta description. Take out time and write unique title tags and meta descriptions for each page, keeping them brief but descriptive. You also want these to be explicitly clear.
As for your keywords, make sure they match your intent and are placed organically throughout the article. Title tags shouldn’t be too long and be unique across all pages.
Title tags, meta description, schema… you also don’t want to forget about image tags.
Make a point to add the alt tags of every image you include in your content. Search bots cannot see the images, but they can read alt tags and any information you add while indexing your web pages.
If you want more guidance on creating good titles and snippets, we’ve got all the tips.
10. making headings too short or too long—and not using them right
Your article headings should give visitors a fair idea about your content.
The Google crawler uses the H1 heading tag to interpret what your content is about. When a content writer uses more than one H1 heading tag in the same content, it confuses the search engine bots about the real heading of the content, which isn’t good news.
Writing confusing short headings will make it difficult for search engines to determine what your content is about. At the same time, you don’t want to make your headings too long, making it dull and draggy.
Another mistake is using too few headings in the content.
Readability is important in SEO. It's why you should break your articles into different sections and make it easily scrollable.
The solution:
Encourage your content writers to write catchy headings that force people to click on the article and also abide by SEO best practices. Have them target different search topics by creating unique headings within an article so that it’s easily scrollable. There should be lots of H2s, H3s, and H4s—but only one H1.
Allow me to explain.
The H1 tag should introduce the topic your page is about, similar to how a title tells the reader about the contents of a book. On the other hand, H2s are like book chapters that describe the main topics you‘ll cover throughout the article.
H3s to H6s are subsequent headers that serve as additional subheadings within each H2, just as a book chapter may be set up by multiple subtopics.

Lastly, try to include targeted keywords in your header tags. Admittedly, headers don’t have as large an impact on your SEO as a backlink from an authoritative site, but Google still looks at them together in context for your page.
11. writing ordinary or plagiarized content
Your audience wants informative and high-quality content that matches their queries and provides them genuine value. Kind of hard to deliver them this if you publish ordinary and plagiarized content.
Google also penalizes websites that are filled with irrelevant content and ordinary writings. If your content isn’t up to the mark, search engines won’t consider your web page as the best-searched result to match the searcher’s query.
Another SEO mistake businesses make with the quality of content is using plagiarized or duplicate content.
If you end up posting copied content on your website, search engines will consider it spam. In fact, Google is particularly stringent about this when determining your content’s ranking in search engines.
Therefore, put efforts into producing plagiarism-free and original content while maintaining a good standard of English. No copy-pasting or making simple alterations to already published content.
The solution:
In SEO, you always want top-quality content.
This means content with organized wordings and sentences, no grammatical errors, and at least 300 words. Always try to create original content by using your own words to explain ideas. If you accept guest posts, be sure to check for originality via an online plagiarism checker like Copyscape.
Don’t post short, indescriptive, and irrelevant content with low readability. It’ll cause Google to believe you don’t have sufficient knowledge about the topic, lowering your SERP rank.
Moreover, if you plan to syndicate content from other websites—or allow other websites to syndicate your content—you need to know about canonical tags.
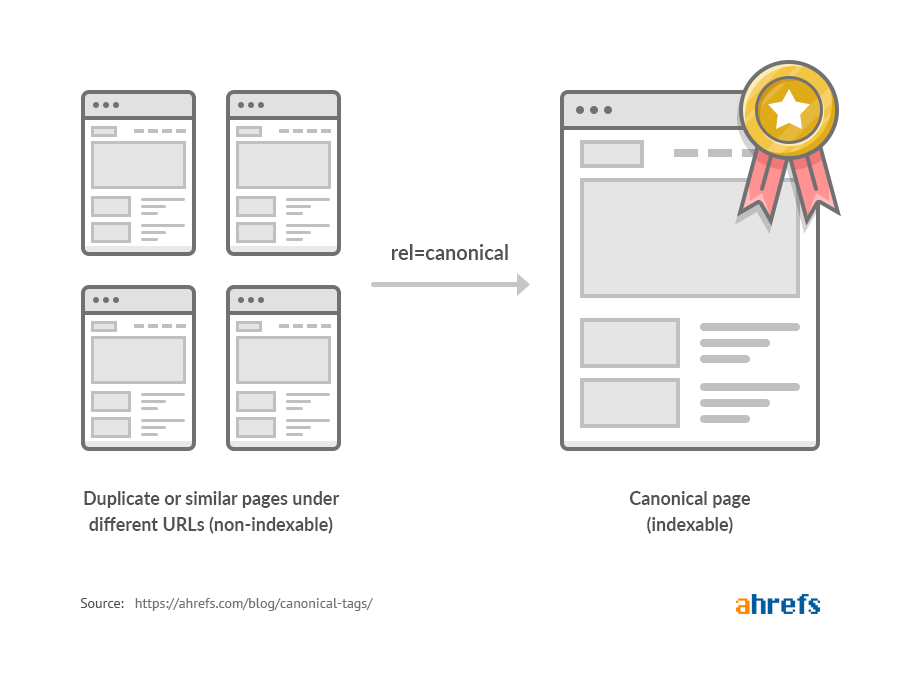
Canonical tags inform Google which is the original in cases of duplicate content and which version of the content to display first in results. Using these tags will allow you to publish your content on other websites while keeping the original page live.
Therefore, if you plan on publishing similar versions of the same content on your website, be sure to specify a canonical version.
Avoid common few mistakes to rank better
SEO can be a lot of work, and it’s certainly not easy to remember all the attached rules, best practices, and tips. But it’s a process you can learn to master through trial and error and making consistent efforts to improve.
You may have already made at least one of the above a few mistakes. The good news is no matter how many errors you make, you can always course-correct and get your website back on Google’s good side.
Look after your SEO and user experience health by using the available tools and applying SEO tips and best practices. Get well acquainted with the challenges and typical SEO mistakes and avoid them in your marketing efforts.
After you implement a company-wide SEO strategy and build a dedicated team, you'll soon see search engine success.
