There are two sides to digital marketing: organic and paid.
The organic side is known as SEO, or search engine optimization. SEO covers all the things you do to optimize your web pages so they rank well in the search engine results pages (SERP).
The point of optimizing for search engines is to get more organic traffic to your website.
But it’s not just more traffic, it’s better traffic.
Google tries very hard to connect searchers with relevant content that answers their search queries. The algorithm looks for relevancy.
Optimize your pages correctly, and Google sees them as relevant and gives them a page one spot on SERP, where more potential customers see it.
The more people who see your snippet (page link + page title tag + page description) in the SERP, the higher the chances are that they will click through to your page.
The more this happens, the more your visibility grows to a prominent spot naturally over time.
This post will walk you through how to optimize your content for search engines so the time you put into SEO returns a worthwhile ROI long term.
Here’s what you’ll learn about specifically:
- what SEO is
- why it matters (reputation and revenue)
- who it’s for (people and algorithms)
- where to use it (content + snippets)
- and what SEO techniques will shine a spotlight on you over your competition (skyscraper, link building, and copycatting)
What this post doesn’t cover is SEO tools.
But worry not, SEO grasshoppers, we’ve got you. Here are 50 of the Best SEO Tools ready to boost your optimization in 2021.
I’ll say it one more time before we get into it:
Search engine optimization (SEO) is what you do to get more traffic.
Do SEO right and you’ll flag the right cars off the highway to your roadside shop. Then it’s up to your content to convert those drivers into fans before they drive away completely happy with what they got. 🥳
Get brand new SEO strategies straight to your inbox every week. 23,739 people already are!Sign Me Up
Let’s break Search Engine Optimization down into its two parts:
- Search engines
- Optimization
What Are Search Engines?
Search engines are software programs that store information about millions of websites online. When a user types a keyphrase into the search bar, the search engine returns results quickly and accurately because search engine crawlers constantly scan the internet indexing pages.
Search engines work by crawling, indexing, and ranking your content, making it easy for searchers to find exactly what they’re looking for—the most relevant information.
Robots look for key indicators called search engine ranking factors. The technical SEO page factors tell crawlers what can be followed and indexed and what can’t be followed (no follow).
Your on-page optimization (keywords, headers, alt text, meta tags, etc.) and internal links make it easy for the crawlers to crawl around making semantic (related) connections between all your pages.
All this information is stored in a massive search engine database. When someone enters a search query, the algorithm scours the database for content that best matches the question and pulls out a list of best results.
But the most important page factor happens after the click: user experience (UX). UX measures how pleased a searcher is with the page they clicked through to. A positive user experience tells Google that your link is a winner.
That’s when your SERP position improves.
What are the search engine ranking factors?
Search engines judge your content according to:
- Quality/authority: is your content set up properly on the page and do other sites with a high domain authority (DA) link to it (backlinks)?
- Technical optimization
- User Experience: is your site designed cleanly, using white space? Is it easy to use and navigate? Are the Call-to-Action (CTA) buttons obvious and meaningful?
Do these things right and search engines show your snippet in a list of other snippets all competing for click attention after a search query.
Your snippet is heavily soaked in SEO. That’s why we teach you how to write a killer snippet in its own post.
Your goal is always to win a sweet spot on the first page of the SERP, ideally in one of the sought-after top three spots.
Why?
Because 65% of all clicks are won by the top three search results of Google.
But aren’t there other search engines?
There used to be quite a few, but Google pushed most of them into oblivion. The search engines that still exist make up a tiny share of the search engine market globally.
But in some corners of the world, they are used exclusively.
These are the top six major search engines used around the world:
1. Google
Google is the goliath search engine.
It is used by 9 out of 10 searchers around the world. It has overtaken the search engine market to such a huge extent that its name is synonymous with searching for something: “Why don’t you Google it?”

Google includes YouTube. It is the grandpappy of all search engines with 92% global search engine market share—that’s 3.5 billion daily searches.
2. Microsoft Bing
Bing includes Yahoo. It has just over 4% of the global search engine market share—about 1.8 billion searches a month (mostly affluent Americans and gamers).
3. Baidu
Baidu captures only 1.6% of the search engine traffic around the world, but it dominates the search engine market in China. 76% of China's 1.398 billion searchers use Baidu.
4. Yandex
Used by less than 1% of the global search market, Yandex is mainly used in Russia and surrounding countries.
5. Duck Duck Go
Flipping the bird to Google’s “invasion of privacy,” Duck Duck Go’s whole deal is to empower less than 1% of the search engine global market to take control of their personal information online. Tired of being tracked? Use Duck Duck Go.
6. Special mention: Ecosia
At only 15 million users, this is the smallest of all search engines in 2021. Why am I mentioning it here at all? Because it’s the only B Lab Certified search engine that donates 80% of its profits to planting trees. We applaud that and give a shout-out to the little eco-friendly search engine that offsets 1kg of carbon with every search term—turning searching for stuff into something that saves the planet. Plus, it’s super cute.
Optimization gets your page ready for Google search engine crawlers that rank your page based on how well you do your SEO.
Rank is very important.
Links on Google’s first page get clicks. Clicks create the opportunity for you to tell customers why and how you’re the best choice for them.
But if you’re not found, all the SEO work you do on your website will be for nothing.
So get found.
What is optimization?
If your snippet stands out in the search engine results pages (SERP), searchers will click your link over your competitors’ links and you’ll win a healthy click-through rate (CTR)—which improves your rank over time.
Getting more clicks drives more search traffic to your site.
Once there, your content had better be brilliant to keep them there. If it is, Google gives you a high dwell time score (which improves your rank).
Your copy should read like a conversation for people but be optimized for search engine crawlers using keywords. The trick is to blend relevant keywords into your content naturally so your copy doesn’t sound like robotic poop.
Humans don’t like reading robotic crap. And crawlers don’t like reading unoptimized pages.
You must do well at both.
If you’ve optimized your website’s pages and posts the right way, you’ll turn those browsers who landed there into leads.
If you’ve optimized your lead the right way, you’ll turn those leads into sales.
More sales means more profit for your company. Ergo, SEO leads to making more money.
But SEO has a lot of moving parts and that’s why embarking on an SEO campaign makes people 😩.
You can minimize the workload by focusing on what things Google finds important. Things like
- high-quality content (which has its own moving parts)
- how you organize that content (we love the hub & spoke model)
- optimizing on-page, off-page, and behind-the-page technical SEO
There’s a lot to do.
SEO is based on high-quality content
On the front face, you make amazing content that answers the searcher’s search query. On the back end, you make sure that amazing content is optimized according to Google’s search engine ranking factors.
Write this on a post-it note and stick it to your screen:
Write content for your customer. But optimize that content for Google.
There is overlap.
At its core, the center of SEO is visibility (for Google and your target audience).
There are techniques you use every single time you put marketing content together. And there are SEO tools that grade if you’ve done things right.
So what the heck is content, exactly?
Content does one thing if done right: it motivates an action that makes your could-be customers happy and makes you money.
Content in physical form is your website, blog, video, podcast, emails, infographics, courses, and downloadables. It’s the helpful stuff you create to connect you with your people by solving their problems better than everyone else out there.
Content is what you get when you put words and design together to reach your marketing goals.
Why bother making content?
Good question.
Unlike paid ads, you can’t buy a spot in organic search.
You have to earn that spot with high-quality content, on-page optimization, off-page optimization, and technical optimization. These things are considered SEO best practices:
- High-quality content gets your message out to the searchers who need you and want to pay you to solve their problems
- On-page optimization tweaks that content for search engine crawlers (HTML markup, anchor text, internal links, etc.)
- Off-page optimization gets other sites pointing to your site as a respected industry authority
- And technical SEO gets the robots applauding how you’ve organized everything and linked things together (robot.txt, sitemaps, schema structured data, page speed etc.)
Follow SEO best practices to score a search engine ranking factor A+. That’s when relevant traffic starts flooding in.
How do you make valuable content?
To be clear:
Ads don’t solve problems. Ads point to content that solves problems.
Say a prospect sees one of your ads (paid marketing) and they click on it. Where do they go? To a landing page.
The landing page is what convinces them to buy in, not the ad; the content makes the sale.
If the landing page looks great and your prospect’s question is answered right away (in the right way), then boom.
The ad put your offer in front of their face, and the landing page sealed the deal.
If you want to build a better relationship with your customers, you invest in their pain point, tell an interesting story that wins mindshare, and give them something they can take away that lightens their load and removes their shoulders from their ears.
What’s the formula for creating great content?
Start with this:
- Put a clear message
- on a clean website (no clutter)
- that has a single action on it (CTA)
- that’s powered underneath by strong optimization.
That formula will get you in front of more of the right customers with Google, so you can show those customers more of your amazing value.
Don’t even begin if you don’t have something truly valuable to offer.
If you don’t know what makes you different, give that some serious thought. Then, give your customers a heads up about what that something is and offer it in a way that they are over-the-top HAPPY to find and use and share on social media.
Valuable stuff is worth spending time (dwell) checking out.
Dwell time increases your click-through rate (CTR) and your interaction stats. All of that activity tells Google you know what you’re talking about. And because of that, you rank higher in the organic search results pages (SERP).
Here are six tips to get you on the right track:
Six content marketing tips:
1. Create original, fresh content
Google improves its search engine algorithm constantly. But one thing Google consistently rewards is fresh content. Add new content (or update old content to keep it relevant) when you see a problem you can solve.
Do keyword research around solving that problem so Google guides customers to your solution.
Trumpets.
How to write your offer (copywriting):
The words are where the magic of SEO happens. Copywriting is art, but it’s also science.
And, no, I’m not just talking about blogging. I’m also talking about your website copy and your landing page copy and the copy on your lead magnets.
Creative words deliver your message to humans. Keywords deliver your message to search bots (also known as crawlers or the algorithm).
People want to read clear answers to their questions and Google wants to determine if your article deserves a spotlight on that topical stage. Getting this mixture right gets more eyes on your article, more shares, and more actions.
Step one: always write first for the customer—it’s the creative side of copywriting that brings your brand to life.
Step two: go back and weave in keywords to get those words in front of more customers (this is called on-page SEO).
The more people you reach, the bigger your opportunity to build trust with a growing audience. When that happens, your reputation earns credibility. And credibility gets clicks.
Trustworthiness powers your click-through rates.
A great message answers questions, educates your people, builds your street cred (industry authority), creates backlink opportunities (SEO), and increases domain authority (SEO).
The right story creates emotional triggers. People click your buttons because they feel you’re the best answer to their problems.
You become a thought leader.
Building industry authority takes time. That authority doesn’t feed dollars into bank accounts—not directly anyway. But it does feed trust into your conversion funnel.
And those loyal fans who trust you, buy your stuff.
Research your keywords, write compelling copy that contains those keywords, keep those words as short as you can, and edit.
Edit again.
Types of content
- landing pages
- blog posts
- email sequences
- downloadable guides
- infographics
- case studies
- lead magnets
- workbooks
- checklists
- quizzes
- courses
Gate each of those content types with a form that drops leads into your marketing machine, so you can make more sales (and the wheels on the bus go wound and wound). Money.
2. Say no to clutter
Clutter is never good. Not in your life and not on your site.
Don’t cram as much crap on there as you can. You’re going for simplicity. Chunk your words into no more than seven brilliant blocks on a page (that’s a UX principle), be picky with your graphics (try Unsplash), and wrap everything in emptiness—pad your words in a healthy dose of white space.
How to design your page
Design is how you make the words look as good as they sound. That means cutting the copy down until it’s naked and wrapping that nakedness in empty space (whitespace).
Viewers appreciate when your site doesn’t look like crap. Minimal design organizes content into easy-to-absorb chunks so your customers know how you’ll solve their problem right away. This is a UX (User eXperience) principle called Miller’s Law.
Ditching clutter draws attention to your value like a key piece of furniture in a spacious Scandinavian apartment. It’s art + psychology + SEO + fashion: sh***y websites aren’t taken seriously.
Design tips
- Pick a mobile-friendly theme designed by professionals, and don’t stray from the original design too much
- Try Canva and Unsplash if you need graphic assets
- Put one headline (H1) and one concise blurb of copy in the hero section (the top part of your page above the fold—the part of the website your viewer sees when they land without having to scroll)
- Make sure the keyword you optimized for in SERP is in that H1 and in that blurb
- Stick a form beside that message and make the form’s action button juicy.
- Give them something irresistible to download. The right giveaway gets your foot in customers’ doors (their inboxes). Then you offer even more helpful stuff by email and your lead gets warmer.
User Experience (UX) tips
If your site looks like crap, the chances of someone bouncing when they land on it goes up. That’s why you put care into design principles like white space, sidebars, progress bars, anchor links, and next steps leaders.
When it comes to user experience, simple is best.
The simpler a site, the faster it loads, the easier it is to understand, the better it converts browsers into buyers.
So, follow this advice:
- Cut down your words (Occam’s Razor)
- Pick no more than three colors
- Use no more than two fonts
- Use one button style (Fitt’s Law)
- Have one call-to-action (Hick’s Law)
- Be picky with your images
- Be generous with your loyalty-building giveaways
- Don’t go for perfection—focus on making it good enough soon enough. (Pareto’s Principle)
- Group your key points together in seven chunks or less (Miller’s Law)
- Pad those points with whitespace so it looks pretty (Aesthetic Usability Effect)
- Put your value statement at the top and bottom (Serial Position Effect) so people know what you’re about when they arrive (primacy), and take it with them when they go (recency)
Lastly, keep the site lean and optimized by compressing your images (try TinyPNG) so it loads fast because If a user has to wait, a user bails (Doherty's Threshold).
All of these UX Laws (and many more) can be found at this site. And all of them are doable.
Get UX down, and you’ll notice some pleasant results in Google Analytics.
3. Nail your UVP
Your value proposition (UVP) is your unique opening shot. It’s your elevator pitch. It’s how you’re different (because sameness is boring). It’s how you solve problems better than your competition.
Tell your audience why you are valuable to them—and actually be more valuable—using a few great words that sound like you.
Make them excited to scroll down. Make Hemingway and Seth Godin proud.
4. Ask for a tiny something in return
Your buttons create actions.
That action can be to contact you, jump to another page, sign up for a valuable course or eBook, or buy your thing.
Make your buttons crystal clear, keep them simple, and guide your customers toward that click. Most importantly, make sure that click makes your customers happy.
You want to give them a relevant result, because the side effect of creating that happiness is sales.
5. Don’t cheat
If you’re going to do something, do it right. Don’t approach your content half-assed and don’t lower your standards. That means actively avoiding black-hat SEO tactics like keywords stuffing, hidden text, and link schemes (buying links) to try to fool the algorithm into thinking you offer more value than you actually do.
That strategy fails all over the place.
It makes you sound robotic and spammy and Google’s algorithm penalizes you when users bounce quickly because your content sucks.
Make 👏 valuable 👏 content.
6. Outsource
Provide the sort of value that makes you a leader in your space. Don’t create a regrettable stew of poetic lingo, tacky imagery, and packed-to-the-nuts design.
We’ve got to create a unique, special experience for them and delight visitors in addition to satisfying their query—Rand Fishkin moz.com
To be blunt...
If writing isn’t your thing, hire a copywriter.
If design isn’t your thing—stop with the beveled and embossed flashing starbursts already 😣—hire a designer. Less-is-more (whitespace).
And if you’re not a webmaster developer, hire someone who is.
Lastly, if you aren’t sure what your CTA (call-to-action) should be or where it should go or what color works best, think about hiring a marketing agency (full of SEO experts) that does.
Or, give it a shot and take a look at these great CTA examples here.
How to organize your site: hub and spoke model
Part of good SEO is optimizing your content. But another part is organizing that optimized content.
The goal here is to structure your site architecture so that users find your content easy to navigate and search engines find your site easy to crawl and index.
The hub and spoke model organizes your site by topic.
Hubs are the general topic pages—the overarching categories. Spokes are articles that focus on one keyphrase under that topic and together explain the hubs in detail.
Internal links tie all the spokes together and also tie the spokes to the hubs.
When your site is organized in this way, users stick around to check out your site and click your links because navigation feels intuitive. The user experience is high.
Google rewards that interaction with a rank boost. That’s when more people see you—which is good for business.
Know what else is good for business? SEO techniques.
SEO techniques
You've read other SEO articles by SEO influencers, but you still don’t get it.
Maybe you lost interest reading about SEO strategy around the 8000-word mark? Thank Brian Dean for that. His Skyscraper Technique powers multi-thousand word blog articles across the internet.
This is just one of many SEO techniques you can use.
Skyscraper Technique
Skyscraper is a powerful SEO technique but it's 😣 time 😖consuming 😩. I know this because I use it—and it takes for-effing-ever to write a detailed, super-useful, covers-every-possible-thing, master guide-like, mountainous blog article.
But Google loves it.
And that's important because SEO is something you do for Google as well as your readers.
Here’s how the Skyscraper technique works:
Step 1: research other articles that write comprehensively about the keyword you want to rank for.
Step 2: Make something even better—and longer.
Step 3: Reach out to other sites and ask for a link back to your content (a backlink). Why would they link to you? Because your massive article is WAY more comprehensive than the current article that site links to.
Use internal links
You might have noticed that there are internal links in this post that point to other KlientBoost pages. We focus on internally linking our pages together because that strengthens our SEO score.
Google sees this technique as adding relevancy to our content—because it actually does that. It’s helpful to point our readers at other useful content related to what they’re reading about.
Spend some time linking from one page to another and you’ll see a boost in your rank.
“Internal linking passes both PageRank (link authority) and relevancy signals. Internal linking is a massively underutilized SEO technique, and it's often enough to see page 2 search rankings jump onto page 1.” SEMrush.
Copy what your competition is doing right
There’s no shame in doing your research. If a competitor ranks high for a keyword you want to rank for, use your favorite keyword research tool to see how they’re doing that.
Then copy that strategy.
But do it better.
Those are three of our favorite SEO techniques.
But here's the thing:
You don't need to scrape the SEO barrel down to its staves.
You should work smarter, not harder.
Cover the bases, use a few tools, and try a few techniques. Add a few more of both as you get the hang of things. Every incremental gain moves browsers closer to becoming buyers.
How do you measure SEO?
After you’ve created high-quality content following SEO best practices, you’ll want to know if all that SEO work paid off.
There are two apps that measure how your site performs in SERP and how it performs on the page:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
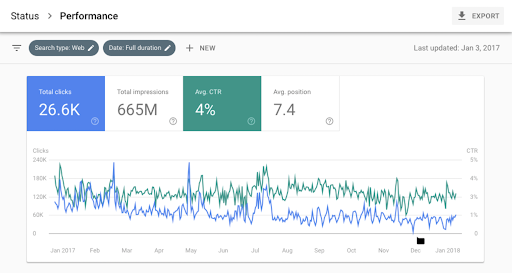
Google Search Console (GSC) evaluates how search engines see your site, showing you things like
- total clicks
- total impressions
- average click-through rate (CTR)
- average position
Google Analytics (GA), on the other hand, shows how users who have clicked through to your site interact with your pages. GA measures metrics like
- number of sessions
- number of pages visited per session
- most popular pages
- number of visitors (users)
- where visitors are coming from
- what device they use to access your site
- session duration (dwell time on each page)
- bounce rate (how fast users click away because your site is boring, confusing, and ugly)
- Conversions
- What sites refer your page
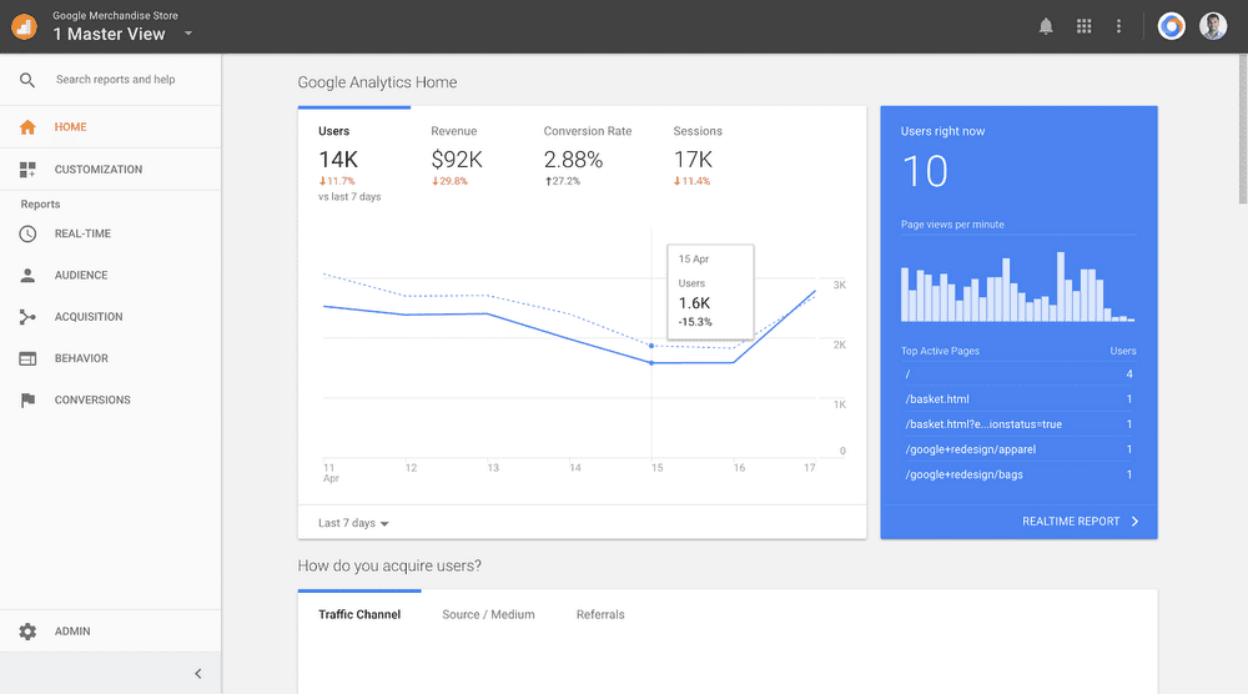
When Google Search Console shows an increase in search performance and Google Analytics shows an increase in traffic and conversions, you know you’re doing SEO right.
SEO for visibility
A clutter-free website that’s organized into hubs with supporting articles that focus on a single long-tail keyword (the search queries your customers use to find you) is a powerful SEO marketing strategy.
But if your site is ugly and disorganized, focuses on low-volume keywords, uses wordy jargon, and fails to solve customer problems, it’s a lost search engine optimization opportunity.
Google decides if you’re the one who gets your face in front of the right people (paying customers) so they throw money at it.
And SEO is how you organically tell Google to give your awesome something some special attention.
SEO takes care of all of the analytical stuff that snags attention and directs customers to your page. SEO is the stuff you add to your page that delivers on what your SERP snippet said it would.
Your keywords (SEO) and snippet (SEO) get prospects to your site. Then your content optimization makes the conversion.
Muck up SEO and no one finds you organically.
And if customers don’t know you exist, it’s all for nothing. Help them find you with strong search engine optimization.
Make amazing content, organize it the right way, and optimize it on, off, and under the page.
Then tell your sales team not to blow it. 😉
And here’s something else to think about:
SEO doesn’t just create a nod of approval with Google. It adds credibility to your brand.
SEO boosts your brand
Digital marketing covers a lot of ground.
There’s PPC (pay per click) ads, CRO (conversion rate optimization), email, and social to plan on top of SEO.
But each of these channels are tied to SEO.
Search marketing goes a long way when it comes to brand credibility. Strong branding contributes to conversions. And conversions drive the entire machine.
When you write excellent content that educates and engages, it puts you up there as an authority in your space. Your fans get to know you because of your brilliant content and they feel good about trusting you after that.
Building trust is a great way to increase conversions.
And conversions are where the money’s at.
What is there beyond SEO?
Yes, SEO powers part of your digital marketing strategy. But there’s another important part you can’t ignore:
Google Ads.
Google Ads is also known as pay-per-click advertising or search engine marketing (SEM). We talk all about the differences between SEO and SEM (and how they are on the same team despite their differences) in our post aptly called “SEO vs SEM.”
Understand that difference and your overall marketing strategy comes together—quick.
Then you can turn your attention to learning How To Do SEO and How to Use Google Ads.